Figure 2.
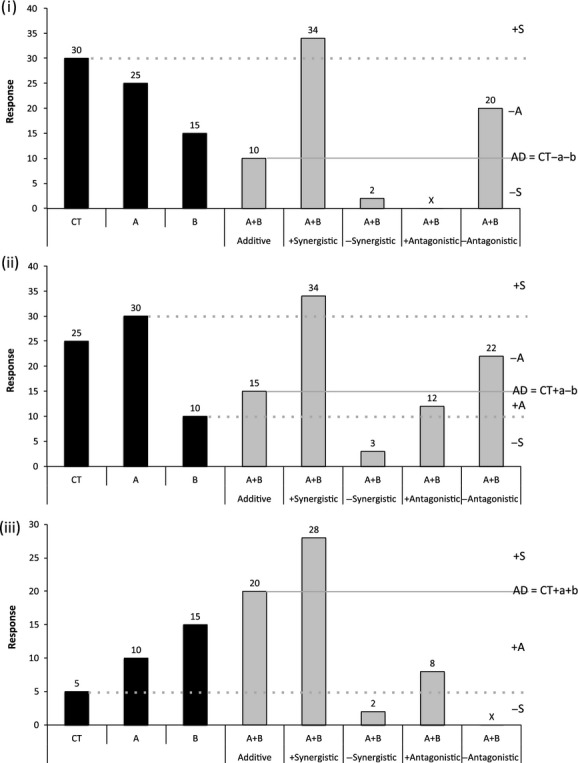
Our conceptual approach to interpreting interaction types from data presented in factorial studies determined from the magnitude and direction of the cumulative effect and interaction effect in absolute terms. Treatments in factorial studies include control (CT), with stressor A (A), with stressor B (B), and with both stressors (A + B). Directional interaction classes are additive (AD), +synergistic (+S), −synergistic (−S), +antagonistic (+A) and -antagonistic (−A) that vary depending on A + B compared to the additive sum (AD) of individual effects for stressor A (a), B (b) relative to the control (CT). The three plots show interaction types that have double-negative (i), opposing (ii), and double-positive (iii) individual stressors effects on the response variable of interest. (X) indicates that an interaction class is not applicable for the interaction type in question. Figure based on a reanalysis of the database of Crain et al. (2008).
