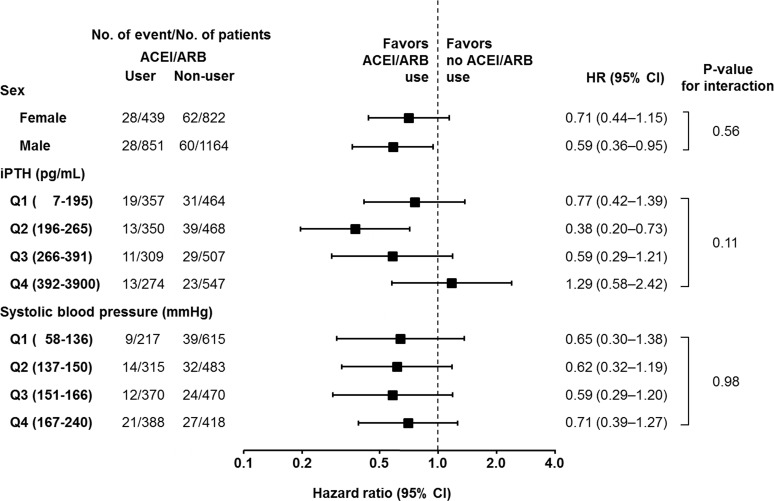
Fig 3. Multivariate-adjusted hazard ratios of hospitalization owing to fractures associated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin II receptor blocker use considering patients with different levels of parathyroid hormone, sex, or systolic blood pressure.
The hazard ratio was obtained from the Cox regression model adjusted for the distribution of age; sex; duration of dialysis; causes of end-stage kidney disease; body mass index; Kt/V; comorbidity of cardiovascular disease or diabetes mellitus; smoking; history of parathyroidectomy; prescriptions of anti-coagulants, vitamin D receptor activators, and phosphate binders; and serum levels of albumin, calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, alkaline phosphatase, and blood hemoglobin, in addition to systolic and diastolic blood pressure and the use of antihypertensive drugs (β-blockers, calcium channel blockers, diuretics, and others). P values for interactions were obtained from the likelihood ratio test. CI: confidence interval, HR: hazard ratio, iPTH: intact parathyroid hormone, ACEI: angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, ARB: angiotensin II receptor blocker.