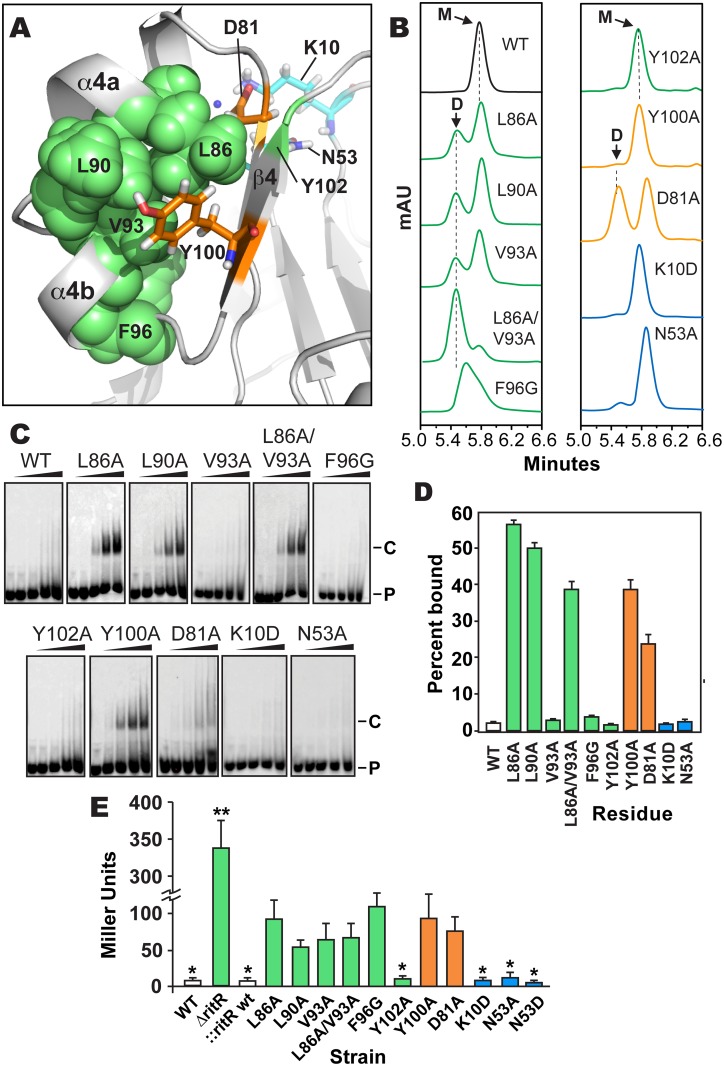
Fig 5. Analysis of RitR mutations.
(a) Cartoon representation of the RitRALR atomic structure depicting important Gate residues (shown in green), the conserved Tyr100 and Asp81 Y/T-coupling residues (shown in orange) and acidic triad residues (shown in cyan). (b) SEC of RitRFL variants (see S6 Fig for protein purity). mAU, milli Absorbance Units; WT, Wild-type RitRFL protein; D, Dimeric form of RitRFL; M, Monomeric form of RitRFL. (c) EMSA shifts of RitRFL variants in the presence of HEX-labeled BS2 33-mer double-stranded DNA oligomer at 0, 0.22, 0.66, 2.2 and 6.6 μM concentrations (left to right). P, Hex-BS2 DNA Probe; C, RitR-(HEX-BS2 DNA) shifted Complex. (d) EMSA quantification of RitRFL variants (2.2 μM) binding to HEX-BS2 DNA. Values represent mean +/- SEM, n = 3. (e) Effect of RitR mutations on Piu promoter activity as measured by β-galactosidase levels (in Miller units). One asterisk indicates a P value of <0.05, and two asterisks a P value of <0.01 as determined by Student’s t-test. Error bars represent mean +/- SEM. t-test comparisons were made using the Y100A mutant as a reference.