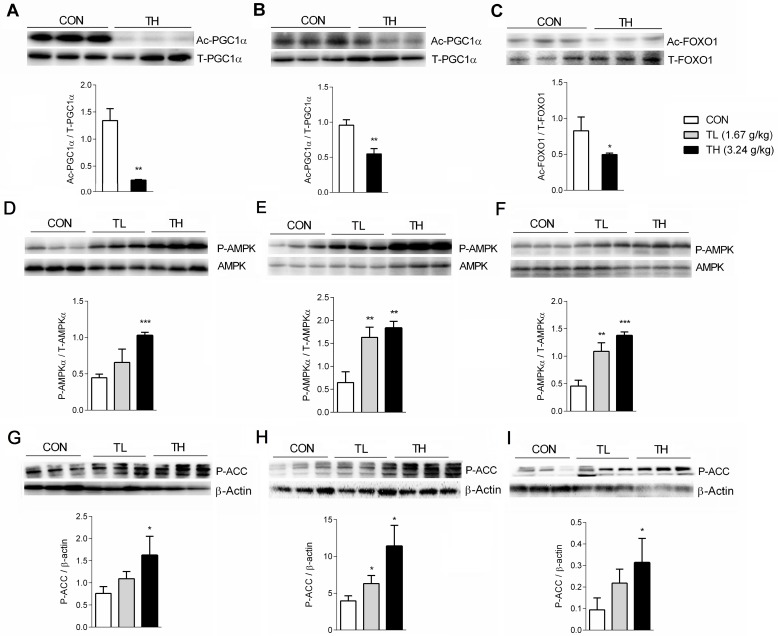
Fig 6. TNK promotes the deacetylation of PGC1α and FOXO1 and activates AMPK signaling.
Acetylation levels of PGC1α in the skeletal muscle (A) and WAT (B) and FOXO1 acetylation level in the skeletal muscle (C) of SHR/cp rats treated with 3.24 g/kg TNK for 7 weeks are shown. Phosphorylation levels of AMPKα in the liver (D), skeletal muscle (E) and WAT (F) of SHR/cp rats treated with TNK for 7 weeks are shown. Phosphorylation levels of ACC in the liver (G), skeletal muscle (H) and WAT (I) of SHR/cp rats treated with TNK for 7 weeks relative to β-actin. Data are shown as the mean ± SD. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. CON. TNK, Tang-Nai-Kang; SHR/cp, SHR.Cg-Lepr cp/NDmcr rat; WKY, Wistar Kyoto rat; CON, control group; TL, low-dose TNK group (1.67 g/kg); TH, high-dose TNK group (3.24 g/kg); WAT, white adipose tissue; PGC1α, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α; FOXO, forkhead transcription factor; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase.