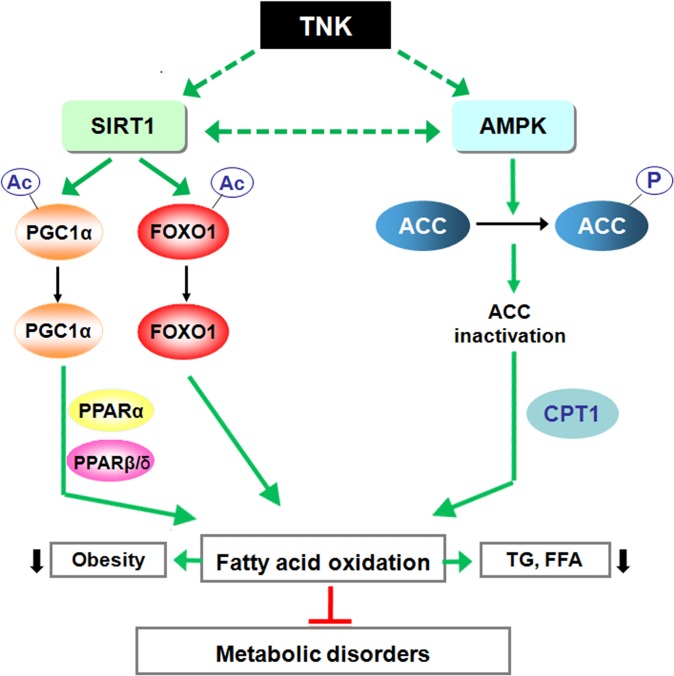
Fig 7. Schematic diagram of the potential mechanism of TNK protection against pre-diabetes and MetS in SHR/cp rats.
TNK activates SIRT1 signaling in SHR/cp rats by up-regulating SIRT1 expression and increasing the deacetylation of PGC1α and FOXO1, two established targets of SIRT1. TNK activates AMPK signaling, as shown by the elevated AMPK and ACC phosphorylation levels in TNK-treated SHR/cp rats. In addition to the up-regulation of PPARα and PPARβ/δ, two nuclear receptors regulating fat oxidation, genes related to fat oxidation and energy expenditure are up-regulated, which in turn leads to improved hyperlipidemia, reduced adiposity and ameliorated pre-diabetes and MetS. TNK, Tang-Nai-Kang; SIRT1, sirtuin 1; PGC1α, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α; PPARα, PPARβ/δ, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-α, -β/δ; PGC1α, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α; FOXO 1, forkhead transcription factor 1; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; CPT, carnitine palmitoyltransferase; TG, total triglycerides; FFA, free fatty acids.