Figure 2.
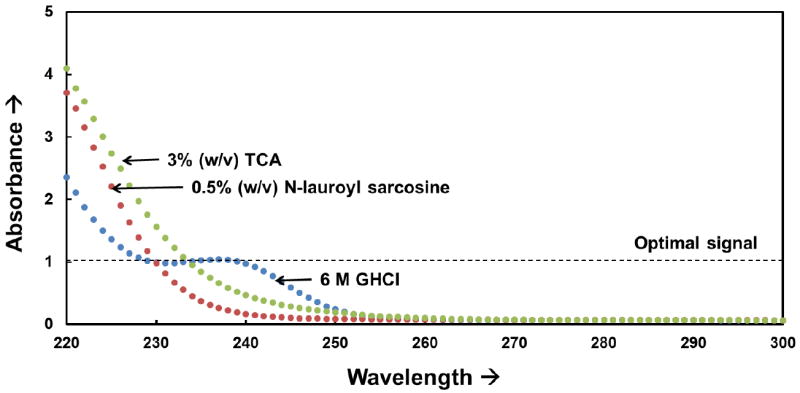
Effective absorbance spectra for different chemical additives (3% (w/v) trichloroacetic acid (TCA, Sigma: T6399), 0.5% (w/v) N-lauroyl sarcosine solutions (Sigma: T7414), and 6 M Guanidium hydrochloride (GHCl, Sigma: G3272)) in deionized water in a 0.1 cm pathlength cuvette. Strong absorbance (> 1) results in signal saturation at high wavelengths, which can prohibit the use of conventional structural analysis algorithms that require CD signal sensitivity over the range of 190 to 230 nm.[1, 12, 33]
