Fig. 5.
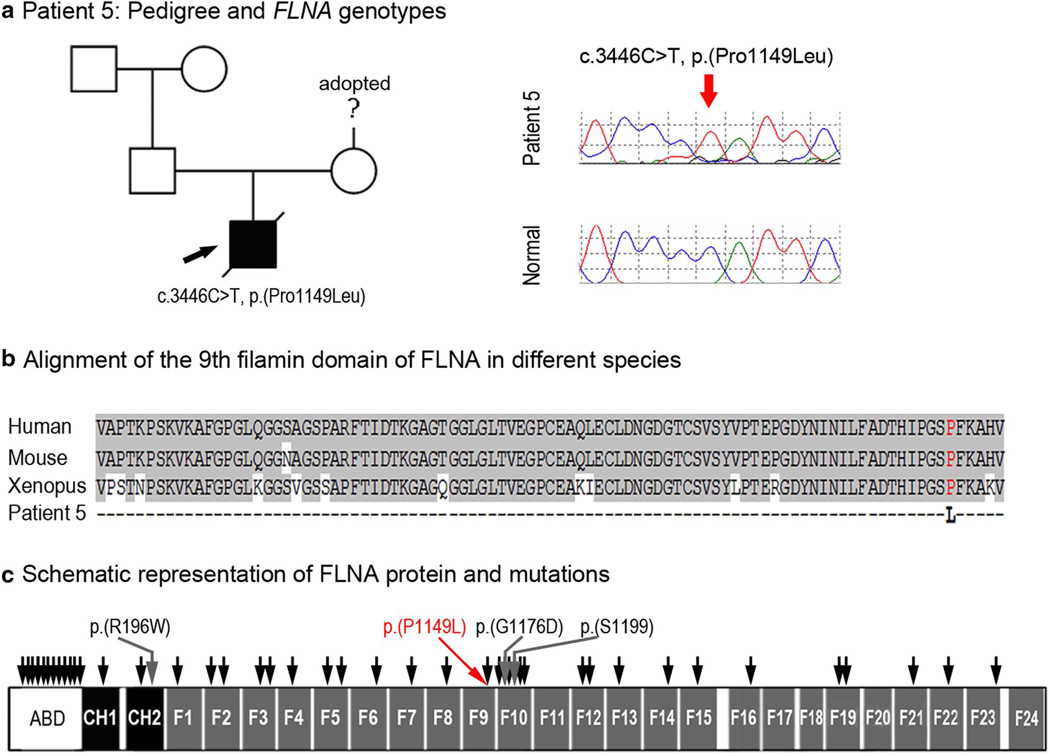
a Patient 5: Pedigree and FLNA genotypes. Pedigree is shown on the left, proband is indicated with a black arrow; DNA chromatograms of FLNA c.3446C>T, p.(Pro1149Leu) mutant and normal alleles are shown on the right. b Alignment of the 9th filamin domain of FLNA in different species. Human (NP_001104026), mouse (NP_001277350), and Xenopus (UniProt ID:F6R7N1) sequences were used for the alignment; proline residue at position 1149 is shown in red font. c Schematic representation of the human FLNA protein and mutations. FLNA domains are indicated according to UniProtKB (P21333): ABD Actin-binding domain, CH1, CH2 calponin homology domains 1 and 2, F1–F24 filamin repeats 1 through 24. The approximate positions of the previously reported FLNA mutations associated with various non-ocular phenotypes are shown by black arrows; mutations associated with ocular phenotypes (please see text) are shown with grey arrows and specified; the p.(P1149L) mutation identified in this study is indicated with red arrow/font