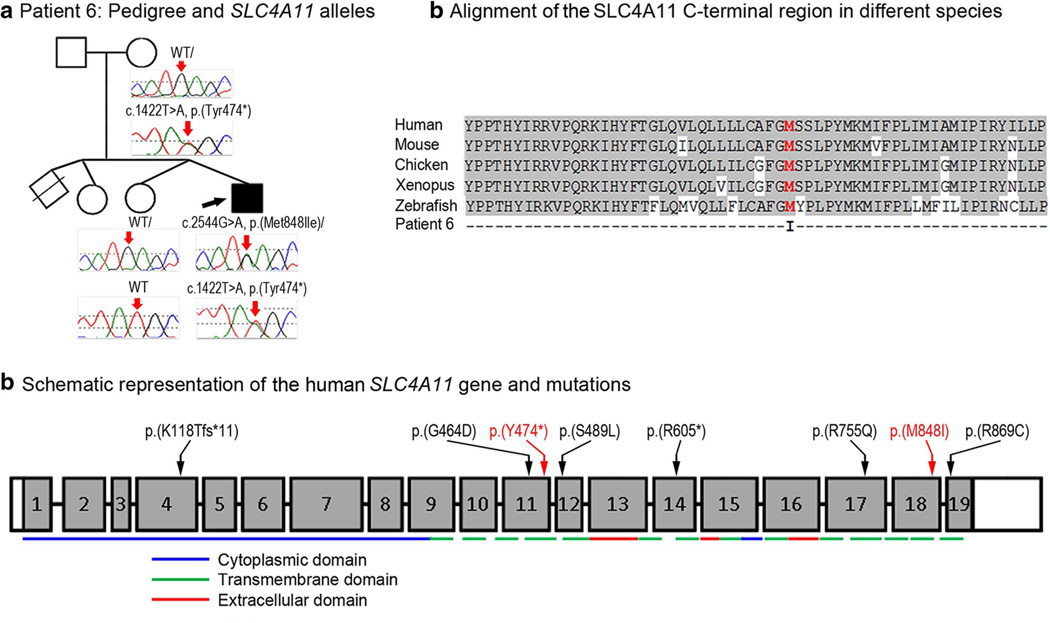
Fig. 6.
a Patient 6: Pedigree and SLC4A11 genotypes. DNA chromatograms of SLC4A11 alleles are shown with positions of c.1422T>A, p.(Tyr474*) and c.2544G>A, p.(Met848Ile) mutations indicated with red arrows; proband is designated with a black arrow. b Alignment of the SLC4A11 C-terminal region in different species. Human (NP_114423), mouse (XP_006499668), chicken (XP_004936340), Xenopus (XM_002936363) and zebrafsh (NM_001159828) sequences were used for the alignment; methionine residue at position 848 is shown in red font. c Schematic representation of the human SLC4A11 gene and mutations. The SLC4A11 exons are shown as numbered grey boxes; positions of cytoplasmic, transmembrane, and extracellular domains encoded by corresponding exonic sequences are indicated at the bottom with blue, green and red lines, correspondingly; positions of the previously described SLC4A11 mutations are indicated with black arrows/font while alleles reported in this study are shown with red arrows/font. SLC4A11 domains and mutations are shown as presented in Vilas et al. (2011) and Vithana et al. (2006)