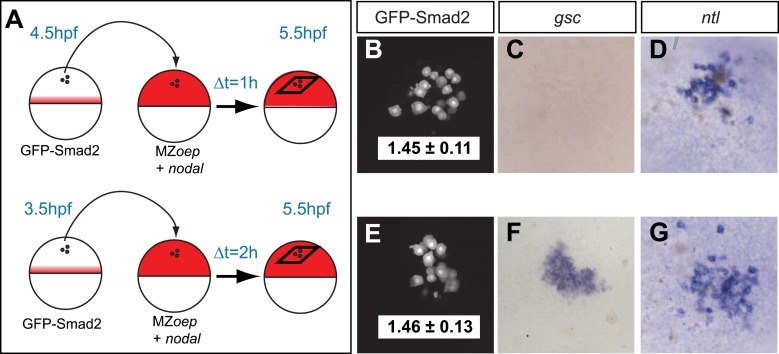
Figure 3. Testing the threshold model.
(A) Schematic of the transplantation experiment. Animal pole cells (black circles) from a GFP-Smad2 transgenic embryo were transplanted into the animal pole of a host embryo that had been injected with mRNA for squint, a zebrafish Nodal gene (red). Host cells were unresponsive to Nodal because they were maternal-zygotic mutants for one-eyed pinhead (MZoep), a cell surface protein required for Nodal signaling. This strategy prevents feedback loops and restricts target gene expression to donor cells. The developmental age of donor cells was matched to host embryos. Black parallelograms indicate imaging plane in subsequent panels. (B–G) Nodal signaling response of donor cells after 1 hr (B–D) or 2 hr (E–G) of exposure to Nodal. (B and E) Projection of confocal stacks of transplanted embryos and associated NC ratio (mean ± std). Activated Smad2 levels are similar in both cases. See Figure 3—figure supplement 1 for time course of GFP-Smad2 N/C ratio. (C and F) RNA in situ hybridization for gsc. (D and G) RNA in situ hybridization for ntl. ntl is expressed after 1 (n = 12/12) or 2 hr (n = 16/16) of Nodal exposure while gsc signal in transplanted cells is only detected after 2 hr of exposure (n = 1/15 at 1 hr, n = 12/14 after 2 hr). Images in B–G are from different embryos. Note that the differences in the duration of Nodal exposure uncouple the activated Smad2 level from target gene expression.