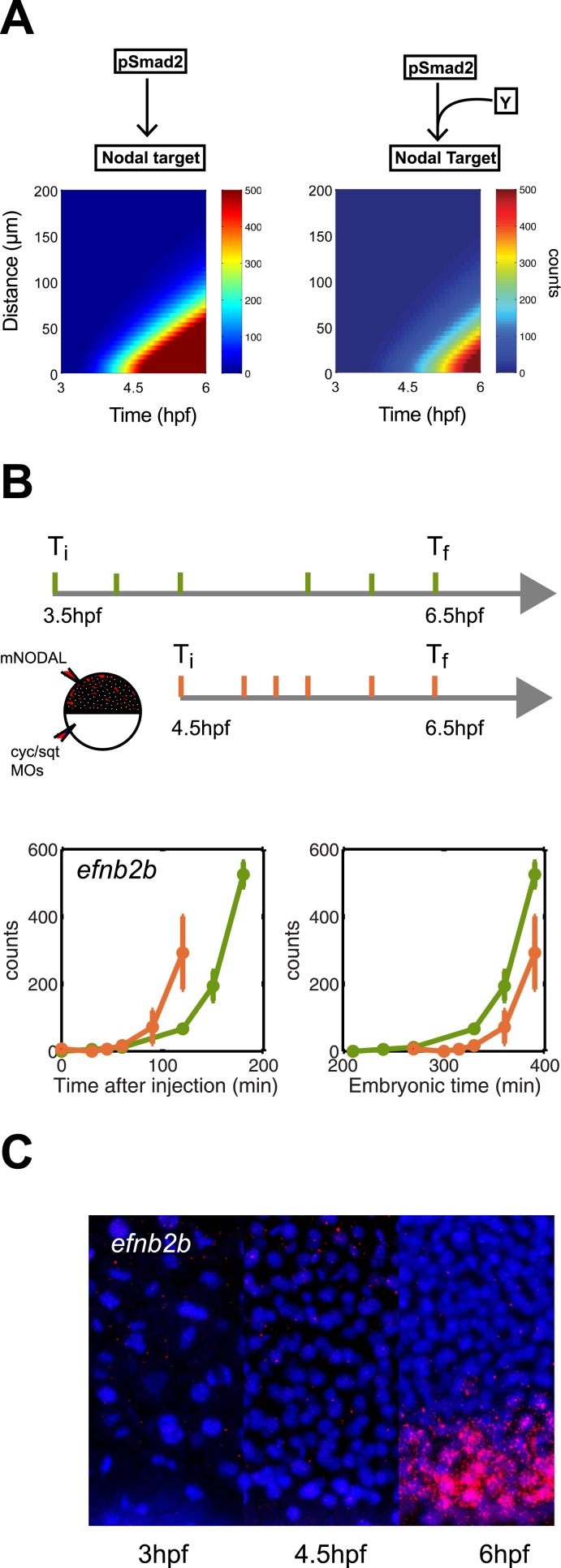
Figure 8. Delayed onset of transcription restricts expression range.
(A) Simulation of efnb2b expression using the kinetic model without (left) or with (right) a co-transcriptional activator Y. The dependence on Y delays the onset of efnb2b expression and reduces its range. (B) Top: Experimental design. Bottom: Time-course induction of efnb2b after injecting recombinant Nodal protein at 3.5 hpf (green) and 4.5 hpf (orange). The induction kinetics of this gene are very slow, but the later Nodal is injected, the faster its induction. Note that counts for the expression of late target genes are higher after early injection compared to later injections. This effect might be due to the fact that after early injections phospho-Smad2 levels are high for a longer period before a gene becomes competent to respond as compared to late injections, when there is a shorter time window of high phospho-Smad2 levels. There might be a priming mechanism in which longer exposure to activated Smad2 increases gene expression when competence is reached. (C) RNA fluorescent in situ hybridization for efnb2b at 3, 4.5 and 6 hpf. Expression of efnb2b is only detected at 6 hpf, although Nodal signaling and the expression of most other Nodal targets commences much earlier.