Figure 1.
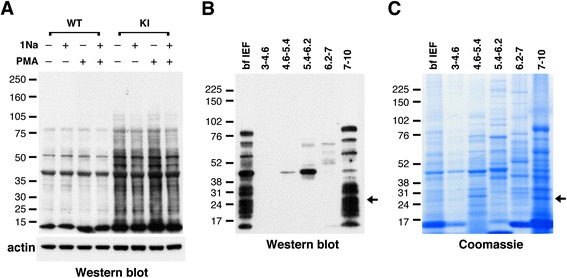
Identification and purification of PKCδ substrates in neutrophils. (A) Western blot with anti-thiophosphate ester antibody showing putative PKCδ substrates in neutrophil lysates from AS-PKCδ knock-in (KI) mice. The bottom panel shows β-actin immunoreactivity in the same samples as a loading control. (B, C) Identification of PKCδ substrates by MicroSol-IEF purification and mass spectrometry. AS-PKCδ neutrophil lysates were incubated with PMA and N6-(benzyl)-ATP-γS, and then thiophosphorylated proteins were alkylated with PNBM and separated by isoelectric focusing in 5 pools as shown. The proteins fractionated before (bf IEF) and after IEF were separated on parallel gels, one of which was subjected to western blot analysis using anti-thiophosphate ester antibody (B) and the other stained with Coomassie Blue (C). The Coomassie-stained protein bands that matched with the immunoreactive bands were excised for analysis by mass spectrometry. The arrows indicate a protein band in the 7–10 pI pool that was identified as LCN2.
