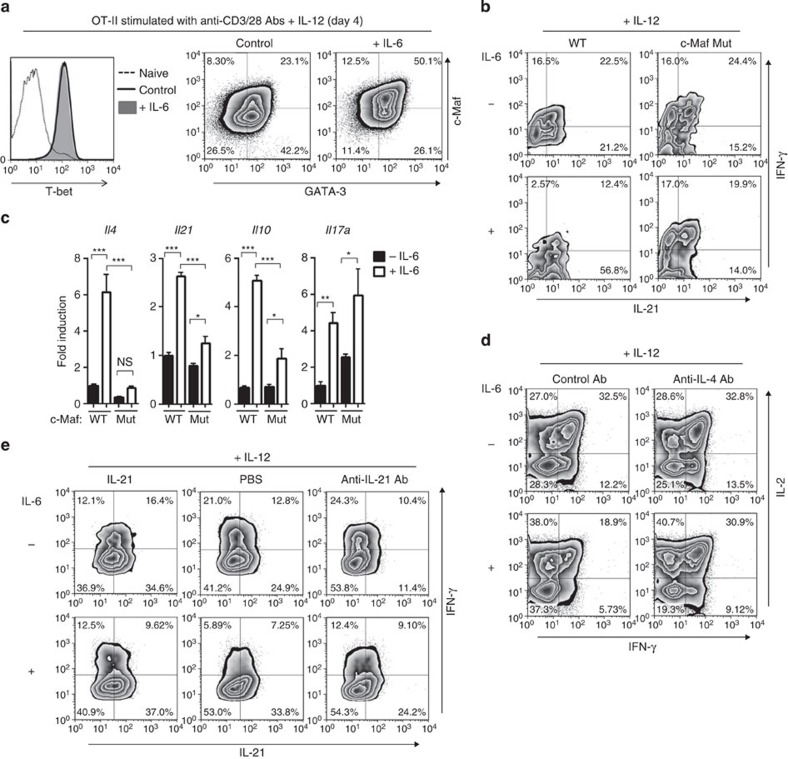
Figure 8. IL-6-induced IL-4/IL-21 production is responsible for the defect of Th1 differentiation.
Young naive CD4+ T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 Abs plus exogenous IL-12 in vitro. (a) Four days after stimulation, expressions of the indicated transcription factors were analysed. (b,c) Naive polyclonal CD4+ T cells from homozygous c-Maf-mutant mice (c-Maf Mut) or littermate control mice (WT) were stimulated in the presence or absence of IL-6. Five days after stimulation, effector cells were re-stimulated with phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate/ionomycin. Representative plots of cytokine-producing cells are shown (b). Indicated cytokine mRNA expression at day 3 was also assessed by real-time quantitative PCR (c). Results are shown as mean±s.e.m. with n=4–6 per group; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, analysis of variance followed by Tukey's post hoc test. NS, not significant. (d,e) Naive OT-II cells were stimulated in the presence of indicated cytokines or Abs. Five days after stimulation, effector cells were re-stimulated and analysed for the ability to produce IFN-γ, IL-2 and/or IL-21. Representative plots are shown. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments. NS, not significant; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.