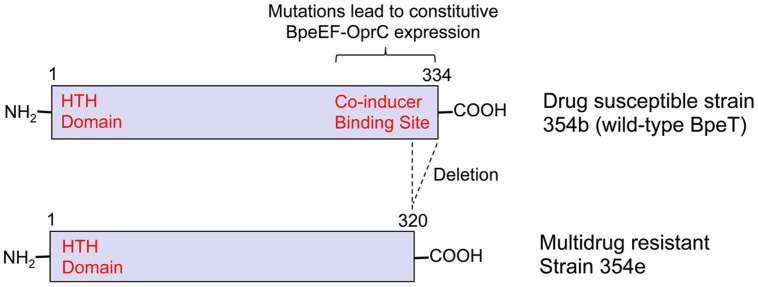
FIGURE 2.
The transcriptional regulator BpeT and locations of mutations causing multidrug resistance due to BpeEF-OprC expression. The figure illustrates the cause of BpeEF-OprC expression leading to a multidrug resistance phenotype due to bpeT mutations by comparing a prototype strain, in this instance a primary melioidosis isolate (strain 354b; Top), and a relapse isolate (strain 354e; Bottom). Strain 354b (Top) expresses wild-type BpeT that exhibits the typical LysR-type regular organization with an amino-terminal helix-turn-helix (HTH) DNA-binding domain and a co-inducer binding site located within the carboxy-terminal half. Point mutations located within the latter domain result in constitutive BpeEF-OprC efflux pump expression. Strain 354e (Bottom) expresses BpeEF-OprC constitutively due to deletion of the last 14 native bpeT codons as a consequence of a 800 kb inversion affecting chromosome 2 (Hayden et al., 2012).