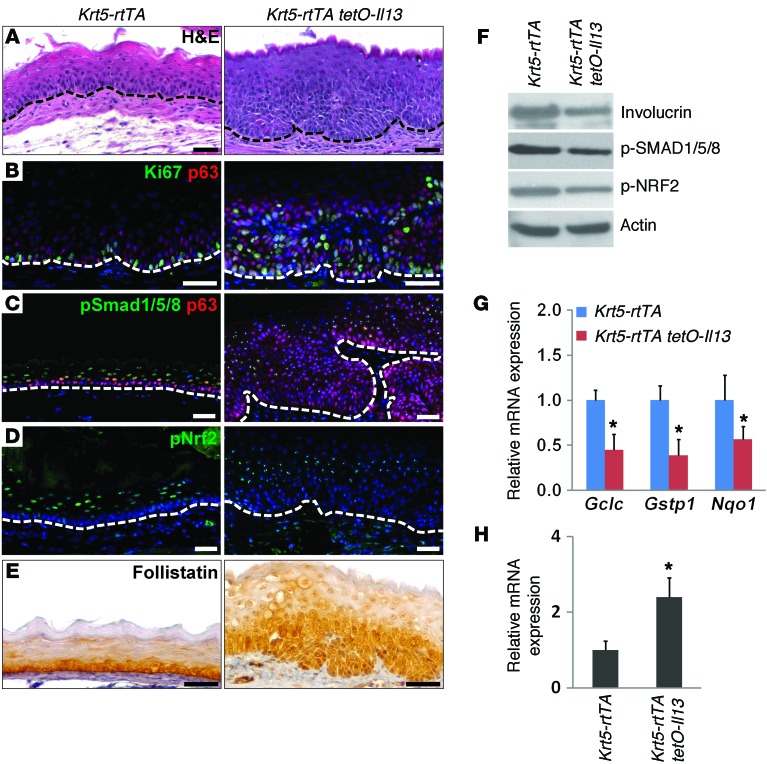
Figure 6. Basal cell hyperplasia is associated with decreased BMP signaling in a mouse model of EoE.
(A) The epithelium was hyperplastic 2 weeks after IL-13 overexpression in basal cells of the esophagus in Krt5-rtTA tetO-Il13 compound mice. (B) Basal cell hyperplasia was accompanied by increased proliferation as indicated by Ki67 immunostaining upon IL-13 overexpression. (C) BMP signaling was reduced in the hyperplastic epithelium. (D) Nuclear localization of p-NRF2 was also reduced after IL-13 overexpression. (E) Follistatin accumulated in the hyperplastic basal cells of the mutant esophagus. (F) Protein levels of involucrin, p-SMAD1/5/8, and p-NRF2 in the esophageal epithelium were decreased upon IL-13 overexpression. Actin was used as a loading control. (G) Transcript levels of Gclc, Gstp1, and Nqo1, genes involved in ROS production and NRF2 signaling, were decreased upon IL-13 overexpression as measured by real-time PCR (n = 5). (H) Fst transcript levels were significantly increased after IL-13 overexpression as measured by real-time PCR (n = 5). Data represent the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 by Student’s t test. Scale bars: 50 μm.