Figure 2.
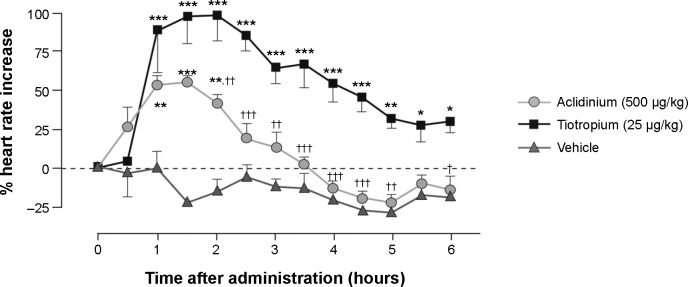
Effect of aclidinium and tiotropium on heart rate in conscious beagle dogs.
Notes: Animals were anesthetized in order to deliver the nebulized compounds or vehicle and were allowed to regain consciousness. The effect on heart rate of a dose 100 times higher than that used to achieve submaximal bronchodilation was assessed continuously up to 6 hours and expressed as a percentage change from baseline heart rate. Data are reported as mean ± SE; n=4 for aclidinium and tiotropium; n=3 for vehicle. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with vehicle; †P<0.05, ††P<0.01, †††P<0.001 compared with tiotropium. Copyright © 2009. Reproduced from The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. Gavaldà A, Miralpeix M, Ramos I, et al. Characterization of aclidinium bromide, a novel inhaled muscarinic antagonist, with long duration of action and a favorable pharmacological profile. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;331(2):740–751.18
Abbreviation: SE, standard error.
