Figure 6.
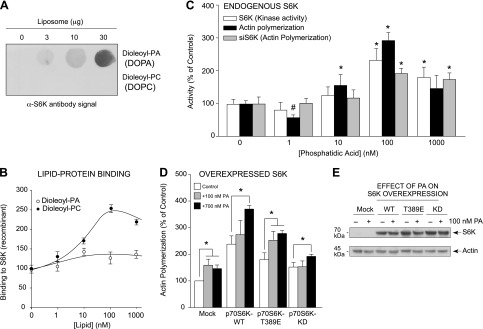
PA and S6K bind together and form a lipid-protein complex that aids in actin polymerization. A, B) In vitro assay of PA:S6K lipid-protein binding. Increasing concentrations of either DOPA or DOPC lipids were spotted onto the PVDF membrane that was incubated first with purified, recombinant S6K protein and then α-S6K antibody. A) The resulting lipid-protein interaction was detected using enhanced chemiluminescence and autoradiography that was then densitometrically quantified in (B). C) Measurements in parallel of actin polymerization and S6K kinase activity from PA-treated samples, similar to (B), using purified, recombinant S6K (kinase activity and actin polymerization) or cell lysates from macrophages that were silenced with 300 nM siRNA specific for S6K and subsequently treated with increasing PA for actin polymerization assays. D) RAW264.7 macrophages were transfected with 2 µg of the relevant S6K plasmid. Two days post-transfection, cells were incubated in the absence or presence of 300 nM PA for 20 minutes, and then lysates were prepared that were used for the pyrene-based actin polymerization assays. Overexpression of kinase-active S6K resulted in increased actin polymerization, while kinase-inactive S6K had no additional effect on actin polymerization. E) WB protein loading controls from samples used in (D) that show overexpression of S6K proteins during 300 nM PA treatment. *P < 0.05, statistically significant increase, between samples and controls. #P < 0.05, statistically significant decrease, between samples and controls.
