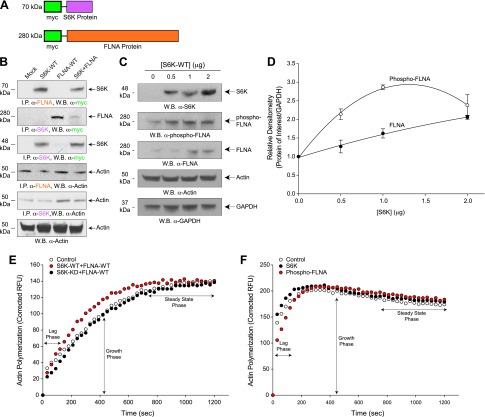
Figure 8.
S6K and FLNA form a protein-protein complex that contributes to increased actin polymerization. A) Schematic cartoon representing the myc tags and both S6K and FLNA protein domains used for co-IP reactions. B) Co-immunoprecipitation assays of protein-protein interaction between FLNA and S6K. RAW264.7 cell lysates that overexpressed mock, S6K, FLNA, or both S6K + FLNA were prepared and immunoprecipitated with rabbit antibodies specific to FLNA (top panel) or S6K (second panel from top) that were then used for SDS-PAGE and subsequent WB and detection using rabbit α-myc antibodies specific for myc-tagged S6K (top panel) or myc-tagged FLNA (second panel from top). Interactions of actin with S6K and FLNA are shown in the panels second and third from the bottom, respectively, indicating that actin is also complexed with the FLNA-S6K heterodimer. Protein loading controls are presented in the lowest panel (WB α-actin). C, D) S6K-WT overexpression increased phosphorylation of FLNA. RAW264.7 macrophages were transfected with increasing concentrations of S6K-WT (0–2 µg) plasmid DNA and 2 d post-transfection cell lysates were prepared that were then used for SDS-PAGE and WB analyses. C) Total S6K, phospho-FLNA, total FLNA, and the actin protein loading controls are shown in the panels from top to bottom, respectively. All samples were run in triplicate. D) Densitometric quantification of samples shown in (C). *P < 0.05, statistically significant, increases between samples and controls. E) Actin polymerization of cell lysates from RAW264.7 cells that were mock-treated (open circles) or overexpressed with 2 µg S6K-WT+2 µg FLNA-WT (red circles) or with 2 µg S6K-KD+2 µg FLNA-WT (black circles). Lag and growth phases of actin polymerization are increased following co-overexpression of kinase-active S6K-WT and FLNA-WT. F) Actin polymerization of 500 ng purified FLNA phosphorylated by 150 ng S6K or S6K alone in a kinase reaction that used cold-ATP in place of radiolabeled [γ-32P]ATP, which was then utilized for the actin polymerization reaction. Significant delay in the lag phase of actin polymerization was evident in response to phospho-FLNA.