Figure 7. Comparison of the ECM structure of Chlamydomonas, Gonium and Volvox.
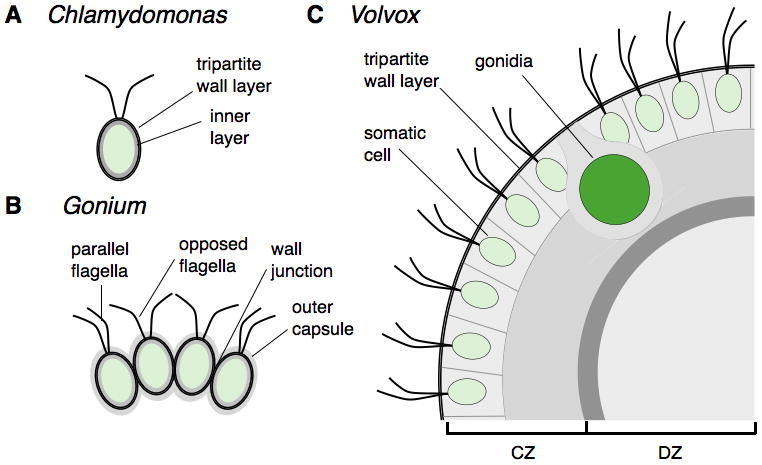
The Chlamydomonas cell wall (A) is composed of an inner layer and an outer tripartite layer that is conserved with other Volvocales (indicated as a black layer around the cell). Individual Gonium cells (B) have an identical tripartite layer and the entire colony is surrounded by an additional outer capsule layer of ECM. Cells are held together by specialized attachments at their wall junctions. (C) Volvox cells are completely embedded in an expanded and compartmentalized ECM with a conserved tripartite boundary layer surrounding the entire colony (instead of individual cells). Inside the tripartite layer of the somatic cells are the cellular zones of ECM and the deep zone of the interior.
