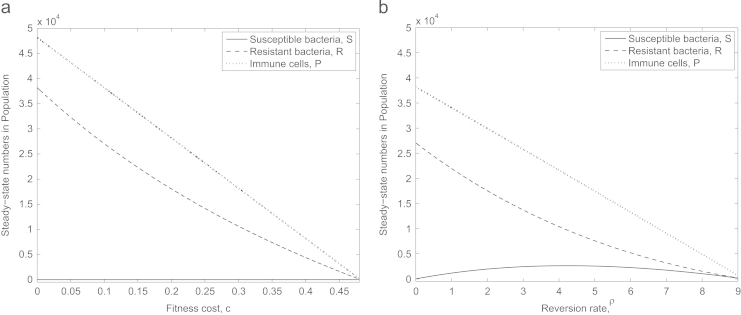
Fig. 4.
Steady-state values of S, R and P in response to varying (a) fitness cost, c, and (b) reversion rate, ρ. Sufficiently high c results in both subpopulations dying out (the susceptible bacteria as a result of the antibiotic and the resistant bacteria because the fitness cost renders them no longer viable) while there exists a range of ρ where both subpopulations can persist in the long-term in spite of treatment by antibiotic.