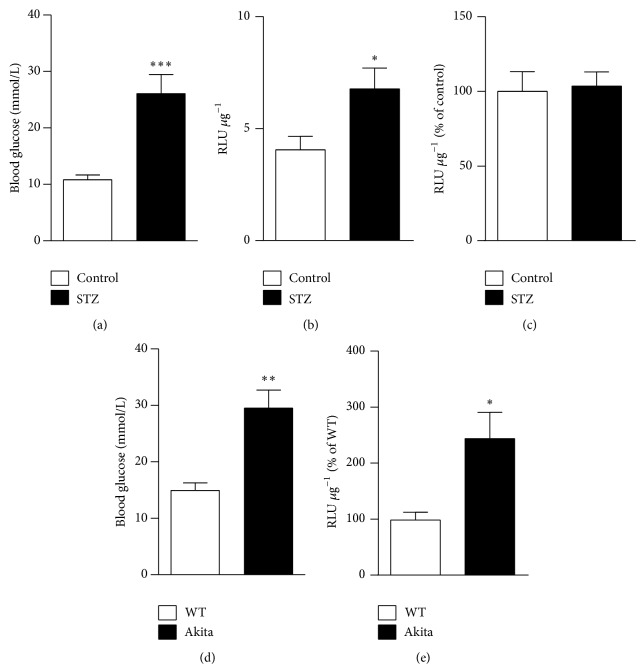
Figure 4.
Chronic hyperglycemia increases NFAT-dependent transcriptional activity in retinal vessels from two different mouse models of diabetes. (a) Blood glucose levels in NFAT-luc mice, treated with STZ (60 mg/kg; black bars) or vehicle (citrate buffer; white bars), measured 12 days after the first injection. (b) NFAT-dependent transcriptional activity (RLU μg−1) in isolated retinal vessels (N = 6-7 mice/group) and (c) in whole retinas (N = 4–7) from the mice in (a). Data is expressed as percentage of activity in normoglycemic control mice. (d) Blood glucose levels in Akita/NFAT-luc mice (black bars) and WT/NFAT-luc mice (white bars) at 6 weeks of age. (e) NFAT-dependent transcriptional activity (RLU μg−1) in isolated retinal vessels from the same mice as in (d). Data is expressed as percentage of activity in WT control mice. N = 11–15 mice/group. ∗ P < 0.05; ∗∗ P < 0.01; and ∗∗∗ P < 0.001 versus corresponding normoglycemic control groups.