Fig 2. VEGF promotes interaction of TRPM2 and c-Src with VE-cadherin.
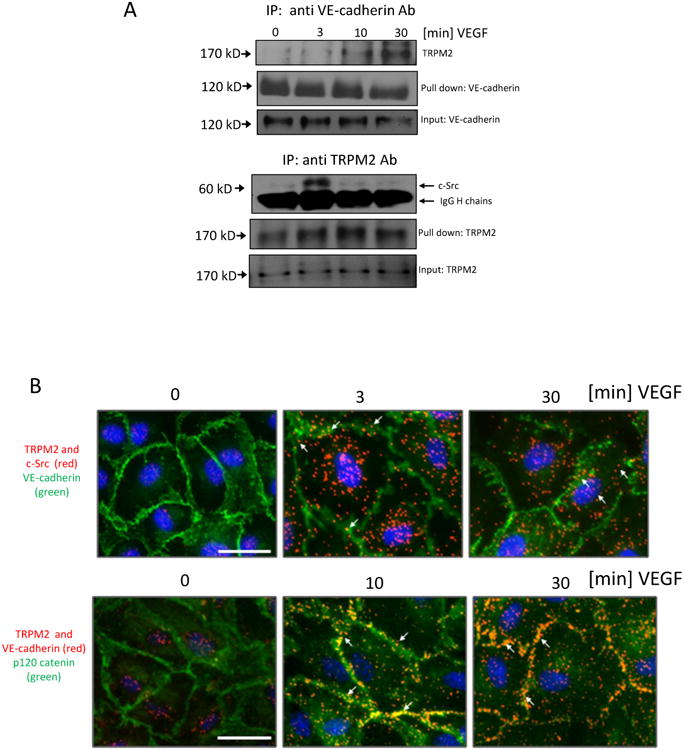
A) Co-immunoprecipitation studies. VE-cadherin was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with anti-VE-cadherin antibody after VEGF stimulation. TRPM2 was detected using anti-TRPM2 antibody. VEGF induced association of TRPM2 with VE-cadherin with maximum response at 30 min. TRPM2 was also immunoprecipitated with anti-TRPM2 antibody after VEGF stimulation and was immunoblotted using the anti-c-Src antibody. Association of c-Src with TRPM2 was observed within 3 min post-VEGF stimulation. Thick bands denote IgG heavy chains; ∼1/10 of original cell lysate was blotted as input control. The experiment was independently reproduced twice.
B) In situ PLA in ECs treated with VEGF at the indicated times. Primary mouse (c-Src) and rabbit (TRPM2) antibodies were combined with secondary PLA probes (Olink Bioscience). The interaction events are visible as red dots, nuclear staining in blue (DAPI), and endothelial junctions are stained with VE-cadherin (green). In another PLA experiment, interaction between TRPM2 and VE-cadherin was determined using primary rabbit (TRPM2) and goat (VE-cadherin) antibodies combined with secondary with PLA probes. The interaction is visible as red dots and endothelial junctions are stained with p120-catenin (green). Scale bar represent 25μm. The experiment was repeated twice with similar observations.
