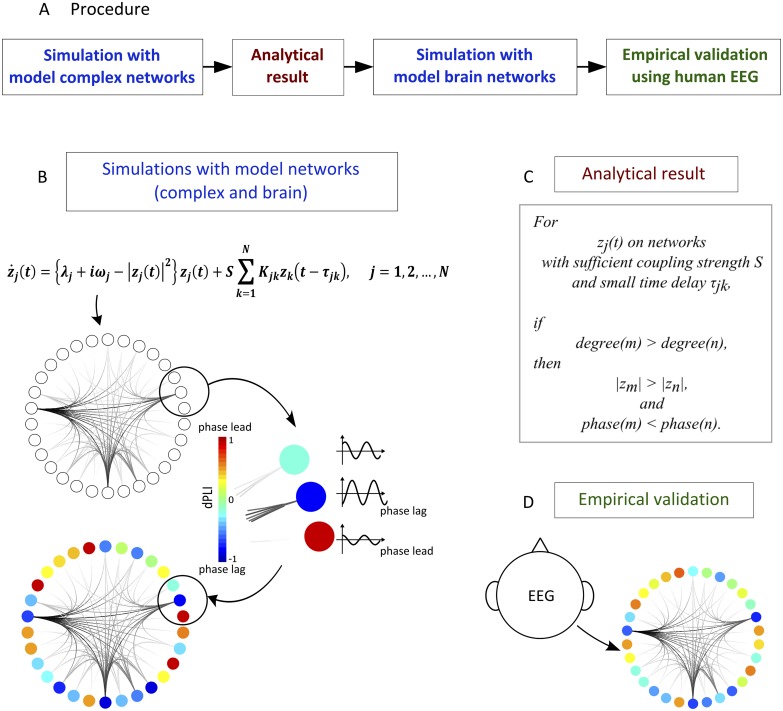
Fig 1. Methodological flow of the study.
(A) The methodology of the study is shown sequentially. We simulated oscillators z j (t) on model complex networks, then derived the analytical result. We applied the same simulation scheme for the human anatomic network and empirically validated the result from human EEG analysis. We made predictions by applying the simulation scheme to the human brain networks. (B) The simulation scheme for networks is shown. Stuart-Landau oscillators z j (t) were applied to the node of each network. We measured whether the signals from each oscillator would phase lead or lag compared to other oscillators using dPLI. (C) We analytically demonstrate that for oscillators z j (t) on networks with sufficient coupling strength S and small time delay τ jk, if degree of node m is larger than degree of node n, the amplitude will be larger and phase lag n. (D) From 64 channel human EEG data, we constructed a connectivity network between each channel and measured phase lead/lag relationships by dPLI.