Figure 4. Activated AMPK inhibits protein synthesis and increases authophagy.
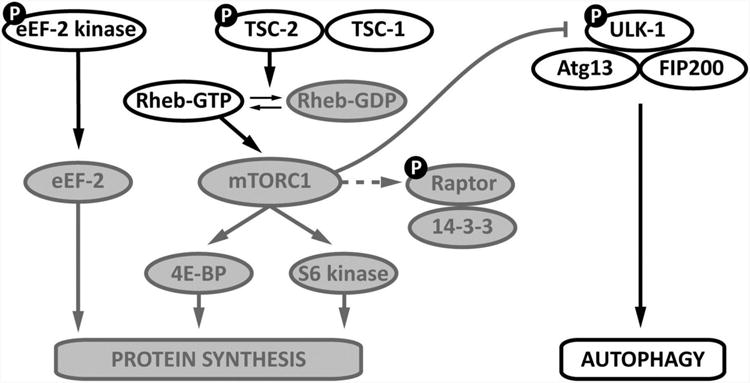
Proteins phosphorylated by AMPK and designated with the symbol “P”. AMPK phosphorylates eukaryotic elongation factor (eEF)-2 kinase, which inhibits eEF-2 activity. AMPK also phosphorylates tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC)-2, which increases the GTP-ase activity of the TSC1-TSC2 complex. AMPK also phosphorylates raptor, which removes it from the mammalian target of rapamycin complex (mTORC) 1 complex. Coordinated TSC2 and raptor phosphorylation result in inactivation of mTOR signaling, which inhibits the function of mTOR in the activation of protein synthesis and inhibition of autophagy. AMPK also phosphorylates Unc-51-like kinase 1 (Ulk1) in the ULK1-Atg13-FIP200 complex to directly promote autophagy. Direct phosphorylation of eEF2 has been shown in the heart, while the other pathways were demonstrated in non-cardiac cells.
