Figure 3.
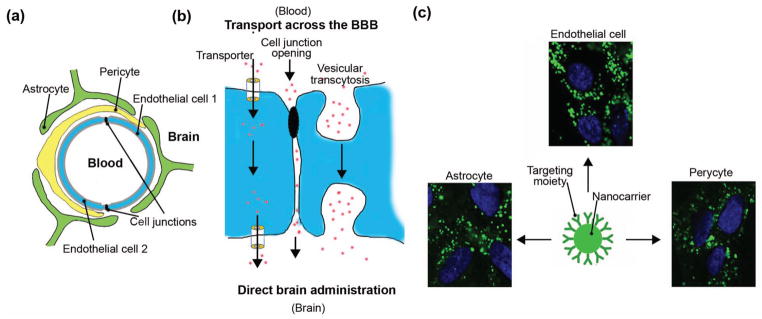
Transport across the blood-brain barrier (BBB). (a) Schematic representation of a blood capillary vessel in the brain. Endothelial cells surround the vessel lumen and seal the passage into the brain by tight cell-cell junctions. Pericytes and astrocytes surround the endothelial lining, further tightening the barrier. (b) Delivery of therapeutics into the brain can be achieved by direct administration through the skull, or by using therapeutics that will cross the BBB. The later involves temporary disruption of the BBB cell-cell junctions (paracellular route) or transport across the endothelial cell (transcellular route), including passage using transporter protein channels or vesicular transcytosis. (c) Nanoparticles coated with ligands which can bind to receptors of vesicular transcytosis (ICAM-1 is shown in this example) results in active uptake by cells of the BBB, including endothelial cells, astrocytes, and pericytes (42).
