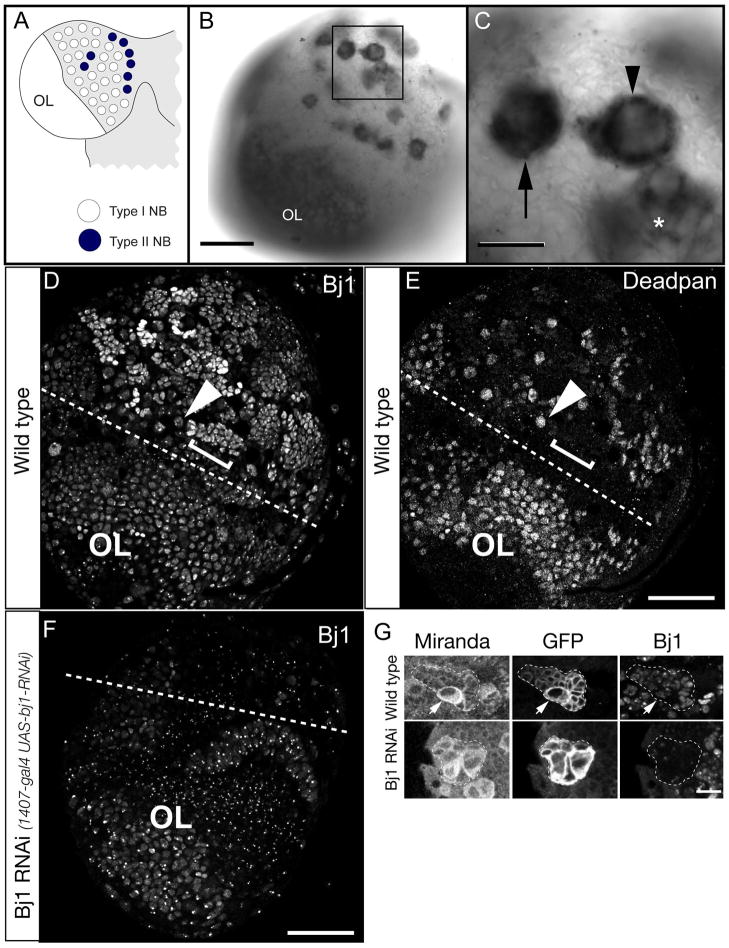
Figure 1. Bj1 RNA is highly enriched in larval type I and II neuroblasts.
(A) Schematic of larval CNS showing one brain lobe. The type I neuroblasts (white) and type II neuroblasts (black); optic lobe neuroblasts are smaller and located more laterally (OL).
(B) Low magnification view of an entire third larval instar brain lobe showing Bj1 RNA enriched in optic lobe neuroblasts (OL) as well as type I and II neuroblasts (boxed).
(C) Enlargement of boxed region in B showing Bj1 RNA is enriched in type I neuroblasts (arrow) and type II neuroblasts (arrowhead), as well as INP progeny of type II neuroblasts (asterisk).
(D,E) Bj1 protein stain (D) and the Deadpan (Dpn) neuroblast/INP marker (E) in a single third instar larval brain lobe. The Dpn+ Bj1+ optic lobe neuroblasts are below the dashed line (OL). A representative type I neuroblast is labeled (arrowhead); neuroblasts show relatively weak Bj1 protein staining. Representative neuroblast progeny, GMCs and neurons, are labeled (bracket); they show relatively strong Bj1 staining.
(F) Bj1 protein in a transgenic Bj1 RNAi third instar larval brain lobe. The central brain is much reduced in size due to Bj1 RNAi causing loss of neuroblasts, whereas the optic lobe is unaffected (because 1407-gal4 is not expressed in this region). Accordingly, Bj1 protein is strongly reduced by only in the central brain. Punctate staining may be background, cross reactivity, or intense Bj1 staining that is less obviously reduced by RNAi.
(G) Bj1 protein staining in larval type II neuroblast lineages (marked with GFP, dashed outlines).
Top row: in wild type, Bj1 is detected in the neuroblast (arrow) and progeny.
Bottom row: Bj1 RNAi reduces Bj1 protein levels.
Scale bar is 50μm in B–F and 10μm in G.