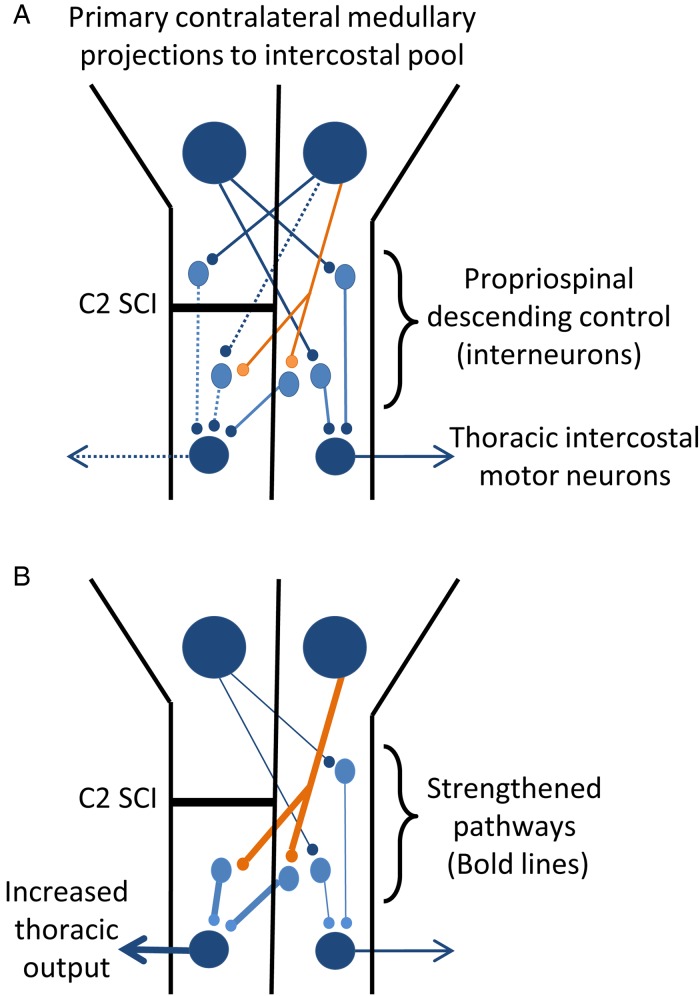
Figure 5 .
A model of neural pathways that project to thoracic motor neurons. The primary projection to intercostal motor neurons arises from contralateral medullary neurons and is polysynaptic. (A) A C2 SCI disrupts the primary signal descending to the thoracic motor neurons ipsilateral to the injury and the thoracic output is silenced. (B) Recovery of motor function most likely arises from the strengthening of established connections from the contralateral spinal cord below the site of injury. A possible pathway for this contralateral, propriospinal input is hypothesized in (B).