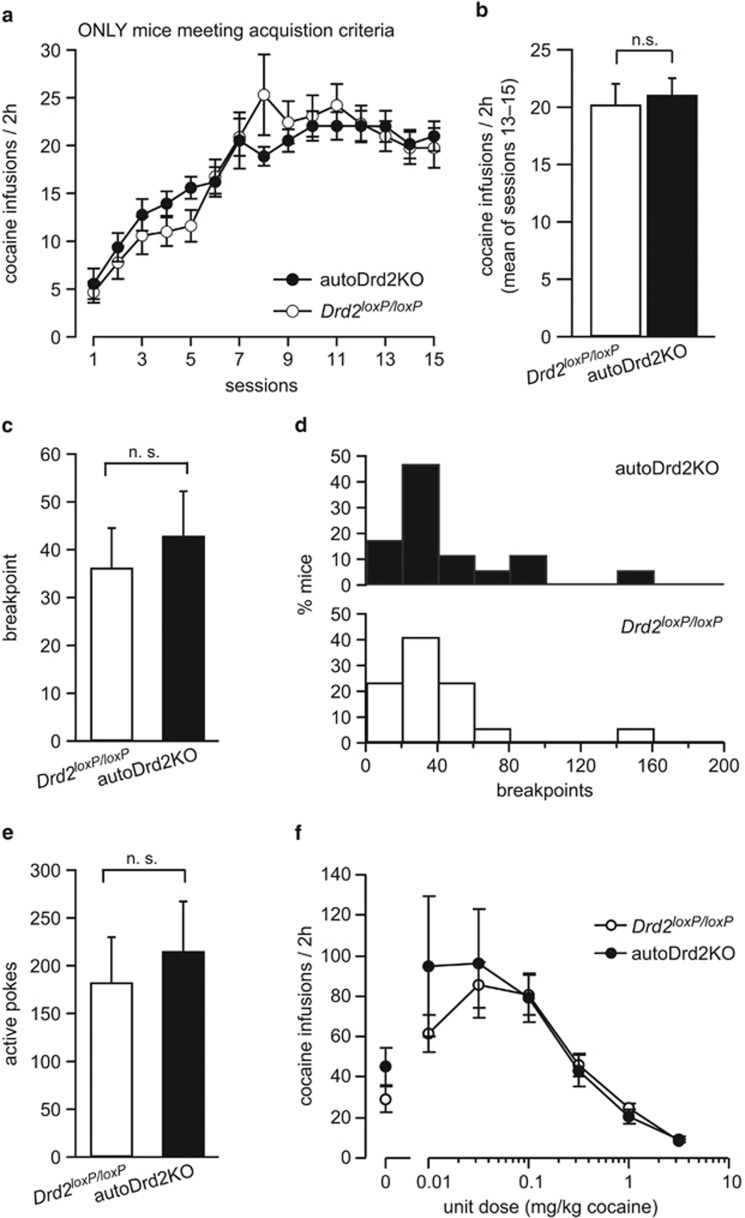
Figure 4.
Once mice acquire, autoDrd2KO mice show similar daily intake, sensitivity, and breakpoint for cocaine. (a) Rate of earned cocaine infusions for autoDrd2KO (solid) and Drd2loxP/loxP (open) mice that met acquisition criteria. (b) Daily cocaine intake during the last 3 training sessions (sessions 13–15) before extinction sessions for all mice that met acquisition criteria; n.s., not significant difference p=0.44. (c) Mean breakpoint value achieved during progressive-ratio session for autoDrd2KO (solid) and Drd2loxP/loxP littermates (open); n.s., not significant difference p=0.59, n=17–17. (d) Distribution of breakpoint values for autoDrd2KO (top, solid) and Drd2loxP/loxP littermate (bottom, open) mice achieved during the progressive-ratio session. (e) Mean number of active pokes performed during progressive-ratio session for autoDrd2KO (solid) and Drd2loxP/loxP littermates (open); n.s., difference p=0.64, n=17–17. (f) Rate of cocaine infusions earned by autoDrd2KO (solid) and Drd2loxP/loxP littermate (open) mice when varying the unitary dose of cocaine infusion; n=6–6. All data, except for (d), are expressed as mean±SEM.