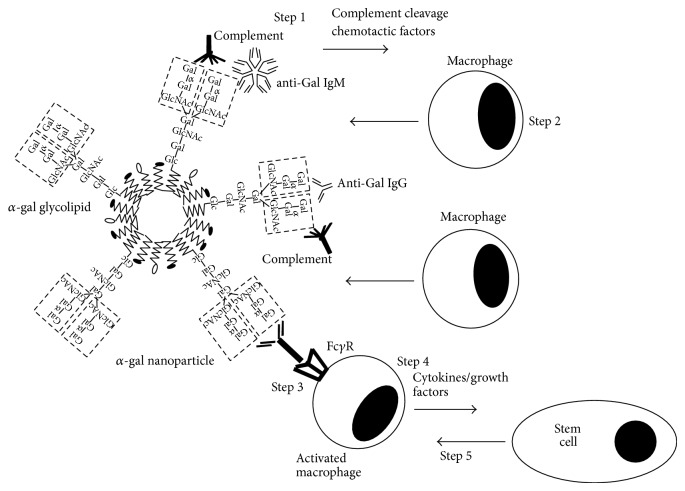
Figure 1.
Illustration of α-gal nanoparticle and the process of accelerated wound healing induced by these nanoparticles. The studied α-gal nanoparticles are comprised of phospholipids, cholesterol, and α-gal glycolipids that carry α-gal epitopes (a representative 10 carbohydrate glycolipid with two branches, each capped with an α-gal epitope, marked by a dashed line rectangle). Application of α-gal nanoparticles to injuries results in the induction of the following sequential steps. (1) The natural anti-Gal Ab binds to α-gal epitopes on the nanoparticles and activates the complement system, resulting in formation of complement cleavage chemotactic peptides. (2) The chemotactic complement peptides induce rapid and extensive recruitment of macrophages into the treated injury. (3) The α-gal nanoparticles activate the recruited macrophages as a result of interaction between the Fc portion of anti-Gal coating the nanoparticles and Fcγ receptors (FcγR) on macrophages. (4) The activated macrophages produce “prohealing” cytokines/growth factors. (5) Secreted cytokines/growth factors further mediate rapid recruitment of stem cells into the injury site. Modified from [21].