Figure 8.
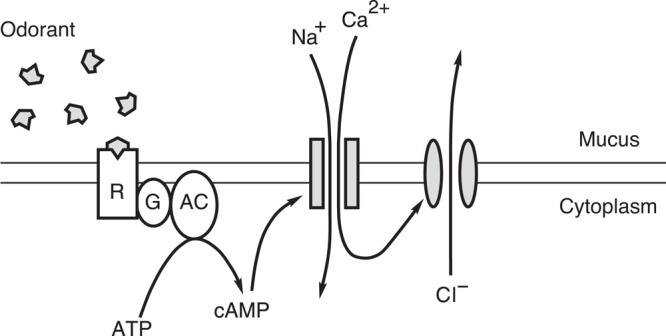
The principal mechanism for transduction of odorous stimuli in vertebrate olfactory cilia. The parallel horizontal lines represent the inner and outer faces of the ciliary membrane of one cilium on an olfactory sensory neuron. The shaded rectangles represent a cation-conducting channel activated by cAMP, and the shaded ellipses represent a Ca2+-gated channel that conducts chloride ions. Abbreviations: AC, type III adenylyl cyclase; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Ca2+, calcium ions; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; Cl−, chloride ions; G, Golf, a G-protein;; Na+, sodium ions; R, odorant-receptor protein. Source: Modified from Kleene (2002) with permission from Elsevier.
