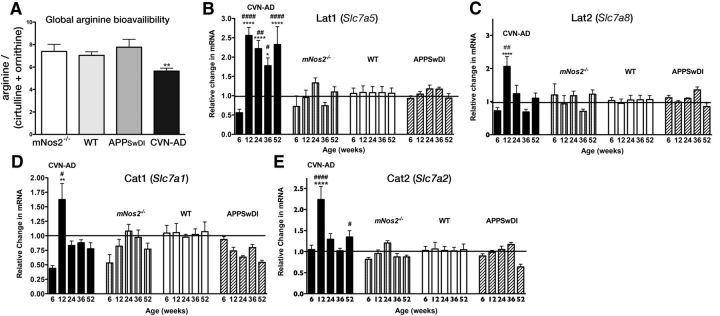
Figure 5.
CVN-AD brains have decreased total l-arginine bioavailability and increased expression of arginine transporters. A, Global arginine bioavailability (arginine/(ornithine + citrulline)) for CVN-AD, mNos2−/−, WT, and APPSwDI mice. Average values (± SEM) per genotype were calculated for individual mice (n = 3–12 mice per group). Amino acid levels were measured using HILIC LC-MS/MS. **p < 0.01 (one-way ANOVA). B–E, Relative gene expression (mean ± SEM) was measured in total brain homogenates from CVN-AD, mNos2−/−, WT, and APPSwDI mice for the neutral arginine transporters Slc7a5 (LAT1) and Slc7a8 (LAT2) (B, C) and for the cationic amino acid transporters Slc7a1 (CAT1) and Slc7a2 (CAT2) (D, E). Samples were analyzed by two-way ANOVA and post hoc multiple comparison test with Bonferonni's correction. *Comparisons between CVN-AD or APPSwDI and WT. #Comparisons between CVN-AD and APPSwDI mice. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001. ****p < 0.0001. #p < 0.05. ##p < 0.01. ###p < 0.001. ####p < 0.0001. n = 4–8 mice per group.