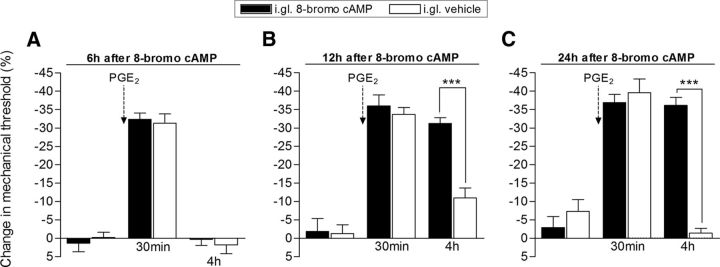
Figure 3.
Time course for the development of hyperalgesic priming induced by intraganglion injection of 8-bromo cAMP. Groups of rats received intraganglion (i.gl.) injection of 8-bromo cAMP (10 μg, black bars) or vehicle. A–C, PGE2 (100 ng) was then injected intradermally into the dorsum of the hindpaw 6 (A), 12 (B), or 24 (C) hours later. Mechanical nociceptive paw-withdrawal thresholds were evaluated before, and 30 min and 4 h after the intradermal injection of PGE2 by the Randall–Selitto paw-withdrawal test. Average paw-withdrawal thresholds measured before, and 6, 12, and 24 h after i.gl. injection of 8-bromo cAMP were as follows: 112.6 ± 0.8 and 116.6 ± 1.7 g, respectively (6 h group); 129.0 ± 3.0 and 128.3 ± 4.0 g, respectively (12 h group); and 126.6 ± 3.9 and 122.6 ± 3.7 g, respectively (24 h group); no significant difference (NS) among these values was observed: after 6 h: t(5) = 2.582; p = 0.4930; NS; after 12 h: t(5) = 0.1147; p = 0.9131, NS; after 24 h: t(5) = 1.054; p = 0.3401, NS; paired Student's t test. For the groups that received vehicle, the average paw-withdrawal thresholds measured before, and 6, 12, and 24 h after i.gl. injection were as follows: 115.6 ± 3.2 and 117.0 ± 2.1 g, respectively (6 h group); 128.3 ± 1.8 and 126.6 ± 3.3 g, respectively (12 h group); and 128.0 ± 4.1 and 118.0 ± 1.2 g, respectively (24 h group). No significant differences among these values were observed: after 6 h: t(5) = 0.7559; p = 0.4838; NS; after 12 h: t(5) = 0.5207; p = 0.6248, NS; after 24 h: t(5) = 2.348; p = 0.0657, NS; paired Student's t test. A, In the group treated with i.gl. injection of 8-bromo cAMP, followed by PGE2 injection into the hindpaw 6 h later, the PGE2-induced hyperalgesia was no longer present when evaluated 4 h after injection (no significant difference was observed when compared with the i.gl.-vehicle group; p > 0.05, two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test, N = 6 paws per group), which is compatible with the absence of priming. B, C, However, when PGE2 was injected 12 h (B) or 24 h (C) after i.gl. injection of 8-bromo cAMP, the hyperalgesia observed was still present at the 4 h time point, indicating that hyperalgesic priming was established (***p < 0.001 when compared the vehicle-treated group at the fourth hour; two-way repeated-measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test, N = 6 paws per group).