Figure 4.
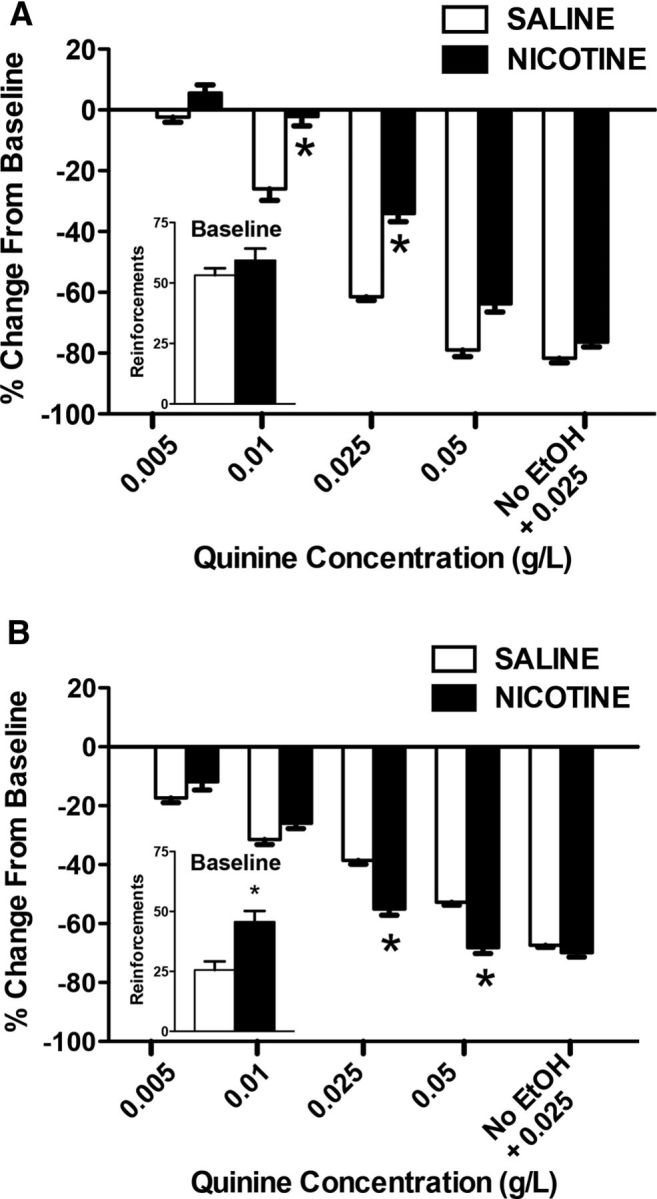
Compulsive-like drinking (i.e., persistent alcohol drinking despite the aversive bitter taste of quinine added to the alcohol solution). The data represent the percentage change from baseline (i.e., lever presses for alcohol alone before adulteration with quinine) in vapor-exposed (A) and air-control (B) rats that were treated with saline (n = 7–9; white bars) or nicotine (n = 7–9; black bars). *p < 0.05, significant difference between saline and nicotine.
