Figure 1.
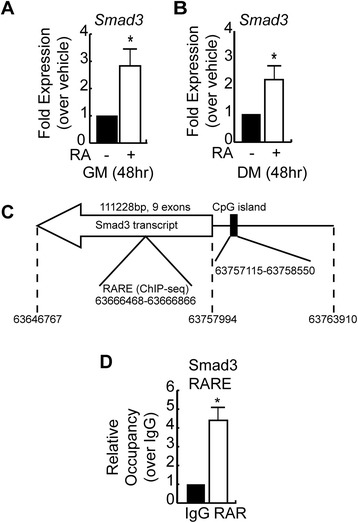
Retinoic acid upregulates Smad3 expression in myoblasts. (A) RT-qPCR analysis of Smad3 mRNA expression in C2C12 myoblasts cultured in growth medium and treated with vehicle or RA for 48 h. Data is shown as fold expression over vehicle-treated condition. Error bars are the SEM, *P < 0.05, n = 3. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of Smad3 mRNA expression in C2C12 myoblasts cultured in differentiation medium and treated with vehicle or RA for 48 h. Data is shown as fold expression over vehicle-treated condition. Error bars are the SEM; *P < 0.05, n = 3. (C) Schematic representation of the mouse Smad3 locus found on the minus strand of chromosome 9 using the Mouse Dec. 2011 (GRCm38/mm10) Assembly. Location of the transcript, including 5′ and 3′ UTRs, is indicated as well as the predicted CpG island (%CG = 65.9%, length = 1,436 bp, ObsCpG/ExpCpG =0.80). The position of a RARE identified by ChIP-seq analysis in ES cells undergoing neurogenesis (GSM482750) between exon 3 and 4 of the Smad3 gene is also indicated. (D) Analysis of retinoic acid receptor (RAR) occupancy of the RARE in the intronic region of the mouse Smad3 gene by chromatin immunoprecipitation and qPCR in C2C12 cells in growth medium. Data represents the mean; error bars are the SEM; *P < 0.05, n = 3.
