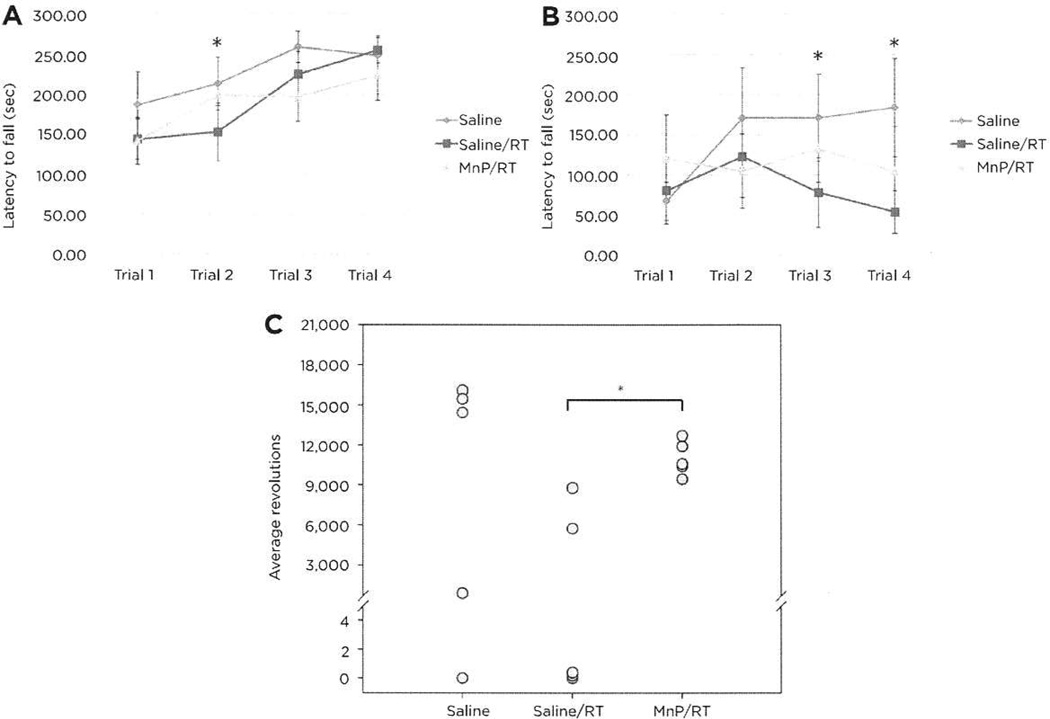
Figure 4.
Neuromotor analyses of mice by rotorod and running wheel. A, accelerating rotorod trials of ten mice per group showed a significant reduction in performance between the saline and saline/RT groups on trial 2 (*, P = 0.034). B, steady-state rotorod analyses demonstrated that the saline controls had longer latencies to fall relative to the saline/RT animals on trials 3 and 4 (*, P = 0.023, P = 0.003. respectively). C. in the voluntary running wheel tests (n = 5), total activity on MnTnBuOE-2-PyP5+/RT group was higher than that in the saline/RT animals (P = 0.034), and the activity of this latter group was marginally lower than that for the saline animals (P < 0.079). Four mice (one from the saline group and three from the saline/RT group) did not run.