Fig 7. Mechanism of melatonin-inhibited branching morphogenesis in the embryonic submandibular gland.
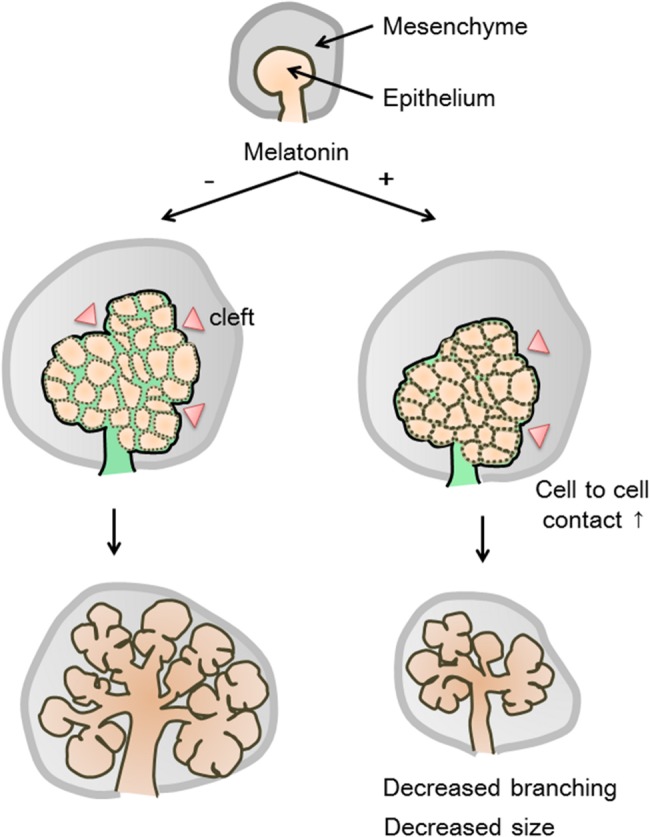
Melatonin changes the morphology of epithelial cells with decreased projections in epithelial cells of the bud. Melatonin increases the direct epithelial cell-cell contacts. The cells are more closely packed and there is less apace between cells. As a result, the size of the organ and the activity of branching morphogenesis are reduced.
