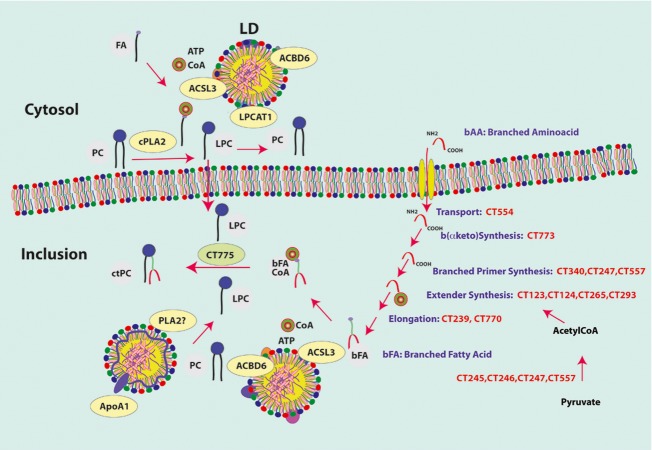
Figure 8.
Proposed model of host PC remodeling in Chlamydia-infected cells. The branched amino acids (bAA) isoleucine, valine, and leucine are imported into the inclusion by the bacterial transporter BrnQ (CT554). Branched α keto acids (α-keto-methylvalerate, α-keto-isovalearte, α-keto-isocaproate) are produced by deamination of bAAs by leucine dehydrogenase (Ldh; CT773). The branched primers (2-methylbutyryl-CoA, isobutyryl-CoA, isovaleryl-CoA) are produced by the Branched α Keto Dehydrogenase complex (PdhA_B, PdhC, LpdA; CT340, CT247, CT557) from the b(α-keto) intermediates. The extender malonyl-CoA is produced by the acetyl-CoA carboxylase complex (AccA, AccB, AccC, AccD; CT123-124-265-293) from acetyl-CoA. Acetyl-CoA is produced from pyruvate by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PdhA, PdhB, PdhC, LpdA; CT245, CT246, CT247, CT557) and is also the primer for de novo synthesis of straight-chain fatty acids. Branched-fatty acids (bFA) present at the sn-2 position of Chlamydia lipids are generated by elongation by FabF (CT770) and FabH (CT239) of the branched primers. Branched FAs are then activated by the human long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase ACSL3 and transferred on lysoPC by the bacterial LPCAT enzyme (CT775). Human acyl-CoA binding protein ACBD6 buffered the lumen concentration of acyl-CoAs to prevent inhibition of CT775. The lysoPC precursor can be obtained by attack of PC of the inclusion membrane and of LDs by cytosolic PLA2 enzyme. LPC could be generated inside the inclusion from PC of the LDs transported in the inclusion by the lipase activity of an unidentified PLA2 enzyme or of the HDL particles recruited in the inclusion. Acyl chains are pictured in green, choline head group in blue, and CoASH in brown. hACBD6, hACSL3, and hLPCAT1 proteins are shown bound to the lipid monolayer surrounding the LDs. A HDL particle is indicated associated to ApoAI lipoprotein. PC, phosphatidylcholine; LDs, lipid droplets.