Figure 6.
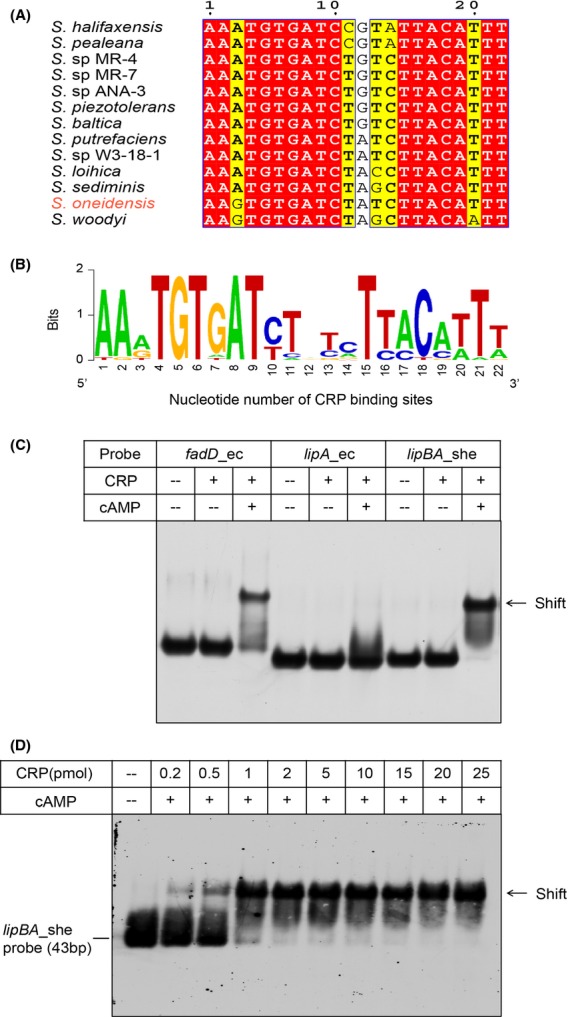
Binding of Shewanella lipBA to the cAMP-CRP functional complex. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of CRP-recognizable sites from Shewanella lipBA operon. Multiple sequence alignment was performed as described in Figure2. Identical residues are indicated with white letters on a red background, similar residues are black letters on yellow, and varied residues are in black letters. Totally, the CRP-binding sites are sampled from 13 different species of Shewanella. (B) Sequence logo for the CRP palindromic consensus sequences. The palindromic sequences used here are identical to those listed in (A), and the sequence logo was generated using WebLogo (http://weblogo.berkeley.edu/logo.cgi). (C) Escherichia coli CRP binds to Shewanella lipBA promoter, but not E. coli lipA promoter. The CRP site of E. coli fadD (fadD_ec) is used as positive control, while the possible CRP site of E. coli lipA (lipA_ec) is referred to negative control (Table2). The plus sign represents addition of the CRP protein and/or cAMP, whereas the minus sign denotes no addition of the CRP protein and/or cAMP. Designations: ec, E. coli; she, Shewanella. (D) Dose-dependent binding of E. coli CRP binds to Shewanella lipBA promoter. The level of CRP protein in (A) is 2 pmol, and the amount of cAMP is 20 pmol. The protein samples were incubated with 0.2 pmol of DIG-labeled lipBA_she probe (43 bp) in a total volume of 20 μL. A representative result from three independent gel shift assays (7% native PAGE) is given. CRP, cAMP-receptor protein.
