Figure 1.
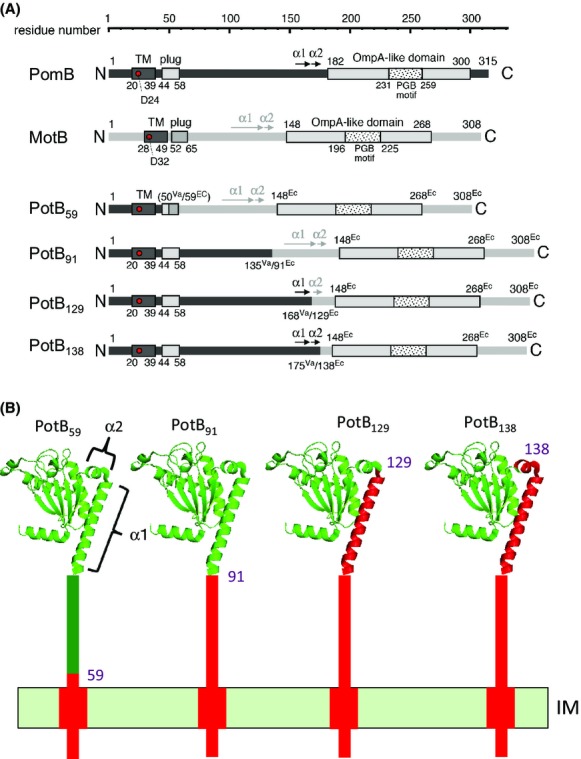
Constructs of the chimeric proteins used in this study. (A) Schematics of the primary structures of PomB, PotB59, PotB91, PotB129 and PotB138. PomB is composed of 315 amino acids and has a single TM domain (residues 20–39) in the N-terminal region, a plug domain (residues 44–58) and a large periplasmic region including an “Omp-A like domain” (residues 182–300). Asp-24, which is essential for ion translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane is shown as a red circle. (B) Topology models of the chimeric proteins. PotB91, PotB129 and PotB138 contain the region prior to the α1 helix of PomB, the region from the N terminal to the α1 helix of PomB, and the region from the N terminal to the α2 helix of PomB, respectively, and the rest of the region is derived from MotB. In the topological models, red indicates regions derived from PomB and green indicates regions derived from MotB.
