Figure 2. Comparison of antidromic volleys in group Ia afferents in a muscle nerve evoked by intraspinal stimuli before, during and after DC polarization.
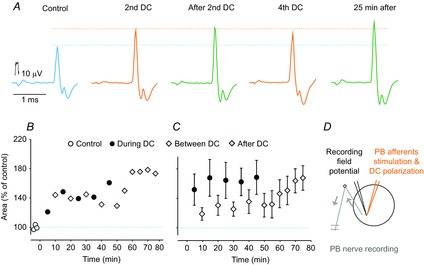
A, records from the PB nerve after constant current intraspinal stimuli (0.1 μA) applied in the PBST motor nucleus in a preparation in which both the L7 and S1 VRs were transected. The records were obtained before, during and after cathodal DC polarization (0.1 μA), as indicated. Averages of 20 records. Lower and upper dotted horizontal lines indicate maximal amplitudes of the volleys evoked before and during the DC application. The latency of the control responses was shortened by 0.13 ms. B, areas of the antidromic volleys illustrated in A at the end of the control, during the series of alternating polarization and between polarization periods and during the post polarization period. C, as in B but for mean areas of antidromic volleys in 7 group Ia afferents. Repeated measures ANOVA indicated a significant effect (P = 0.0022; F14,84 = 2.74); Tukey's post hoc HSD test revealed no significant differences between the points. D, stimulation, polarization and recording sites. Arrows indicate the direction of the neural traffic.
