Fig. 5. Identification of the H+-sensitive lysine residue.
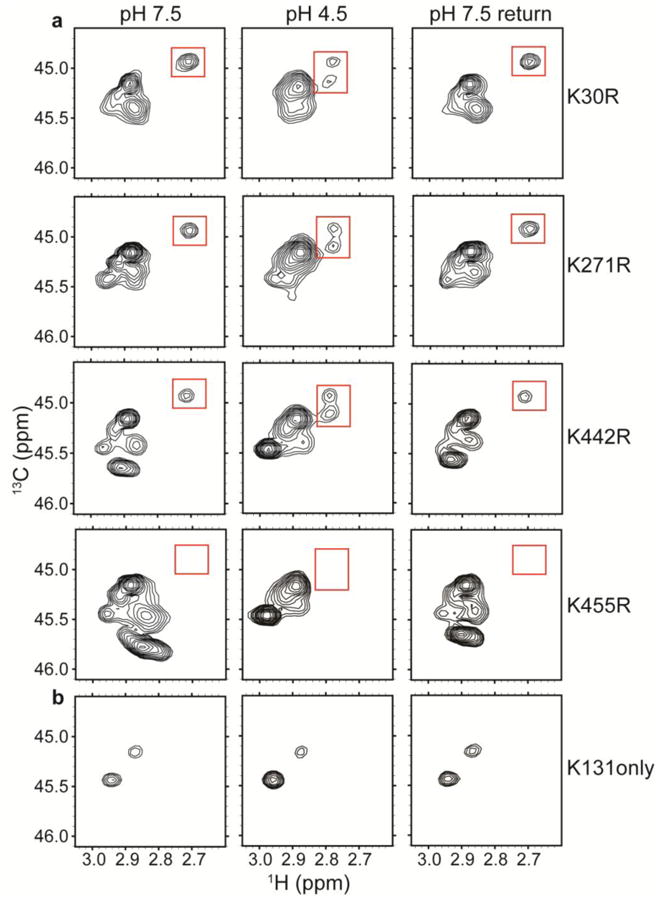
a1H-13C HSQC spectra of methylated ClC-ec1 Lys-to-Arg mutants: K30R, K271R, K442R, and K455R. Unlike the channel-like mutant, these mutants maintain the spectral dispersion observed in WT ClC-ec1. Because Arg residues do not become 13C-methylated, these spectra allow assignment of the peak of interest (highlighted by the red boxes) to K455.
b1H-13C HSQC spectra of “K131 only”, a mutant in which all other Lys residues have been mutated to Arg. The minimal H+-dependence indicates that this region of the protein (Figure 2c) is not undergoing large H+-dependent conformational change.
