Fig. 6. Functional characterization of reductively methylated ClC-ec1.
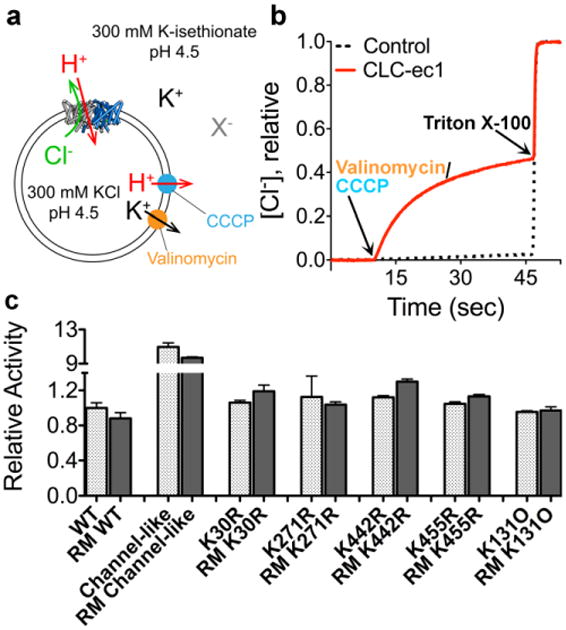
a Schematic outline of the Cl- flux assay. ClC-ec1 is reconstituted into liposomes at high [KCl], and then the extravesicular solution is exchanged for a low-[KCl] solution (replacing Cl- with the impermeant isethionate, “X-”). Bulk Cl- efflux through ClC-ec1 is initiated by valinomycin (a K+ ionophore) and CCCP (a H+ ionophore) to dissipate the electrical potential. Extravesicular [Cl-] is monitored using a Ag/AgCl electrode.
b Representative raw data traces for WT ClC-ec1 (red) and control liposomes (containing no protein) (black dashes). At the end of each experiment, the detergent Triton X-100 was added to lyse the liposomes and release all of the Cl-.
c Summary data for reductively methylated (RM) proteins studied here. The relative turnover rates (normalized to WT unlabeled ClC-ec1) were calculated from the initial slope (Δ[Cl-]/Δt) after addition of Vln/CCCP, and averages ± SEM (n=3 to 6) are reported.
