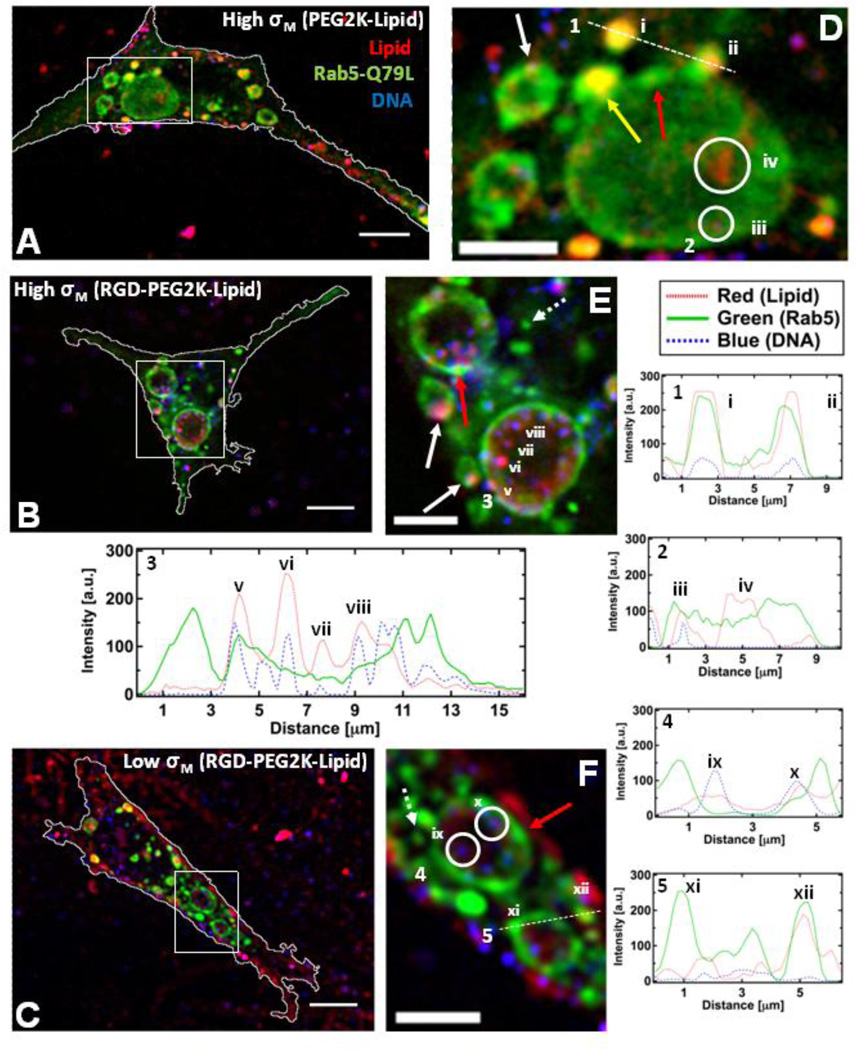
Figure 5.
Colocalization of CL-DNA NPs and giant early endosomes (GEE). Rab5-Q79L inhibits endosome maturation, showing large (>5 µm) endosomes with spatially resolvable NPs. Nearly all intracellular CLDNA particles are found within Rab5-Q79L-GFP labeled endosomes. (Red – TRITC (Lipid), Green – GFP (Endosomes), Blue – Cy5 (DNA)) (A, B, C) Fluorescent micrographs and cell boundaries (white outlines) of L-cells after 1 hour of incubation with (A) PEGylated High-σM NPs (MVL5/DOPC/PEG2K-lipid at a molar ratio of 50/40/10), (B) RGD-tagged High-σM NPs (MVL5/DOPC/RGD-PEG2K-lipid at a molar ratio 50/45/5) and (C) RGD-tagged Low-σM NPs (DOTAP/DOPC/RGD-PEG2K-lipid at a molar ratio of 30/60/10), (D, E, F) High magnification of boxed regions in (A, B, C). (1–5) Intensity profiles of labeled scans from high magnification regions. Intensity profile 1 and 2 show NPs (i, ii, iii) and liposomes (iv) found in EEs and GEEs. Intensity profile 3 shows clear evidence of individually resolvable NPs (v, vi, vii, viii) inside the lumen of the GEE. Intensity profile 4 shows two dim NPs (ix, x) inside a GEE. Intensity profile 5 shows GFP-rich region of the GEE membrane (xi) and a cationic liposome within an EE (xii).The yellow arrow in (D) points to a EE containing a NP fusing with a GEE. Red arrows in (D, E, F) show GFP-rich regions of the GEE membrane. Dashed arrows in (E, F) show smaller EEs similar to what is observed with wildtype Rab5. Solid white arrows in (E) point to clear examples of NPs adhering to the GEE membrane. Scale bars in (A, B, C) and (D, E, F) are 10 µm and 5 µm respectively.