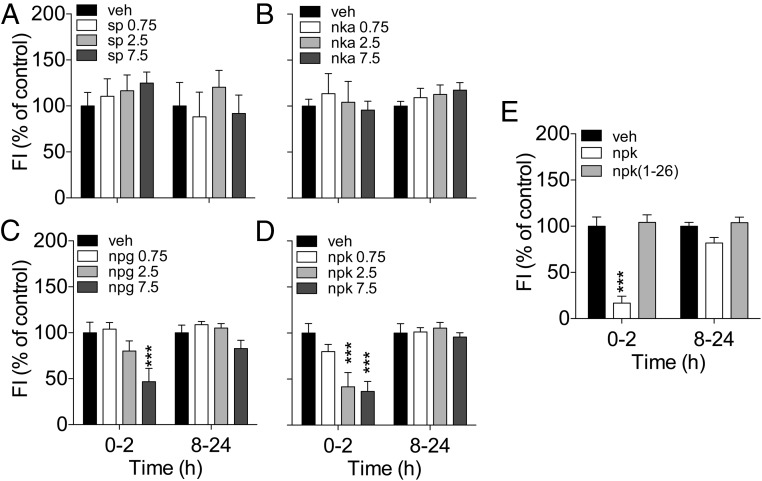
Figure 2.
Effect of acute icv injection of TAC1-derived peptides on food intake on chow-fed Long-Evans male rats. A–D, Food intake change after icv injection of SP (A), NKA (B), NPG (C), and NPK (D) at doses of 0.75, 25, or 7.5 nmol in overnight-fasted rats. Neither SP (A) nor NKA (B) affect food intake at any of the doses tested. C, NPG reduced 2-hour food intake when injected at the dose of 7.5 nmol (P < .001). D, NPK reduced 2-hour food intake when injected at doses of 2.5 and 7.5 nmol (P < .001). E, The loss of the 10-amino acid tachykinin consensus sequence at the carboxyl-terminus eliminated the ability of NPK to reduce feeding when administered at a dose of 2.5 nmol. The average 0- to 2- and 8- to 24-hour food intake was 6.4 and 18.4 g, respectively. ***, P < .001 vs vehicle, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test. Data presented as mean ± SEM, n = 7–10.