Fig. 1.
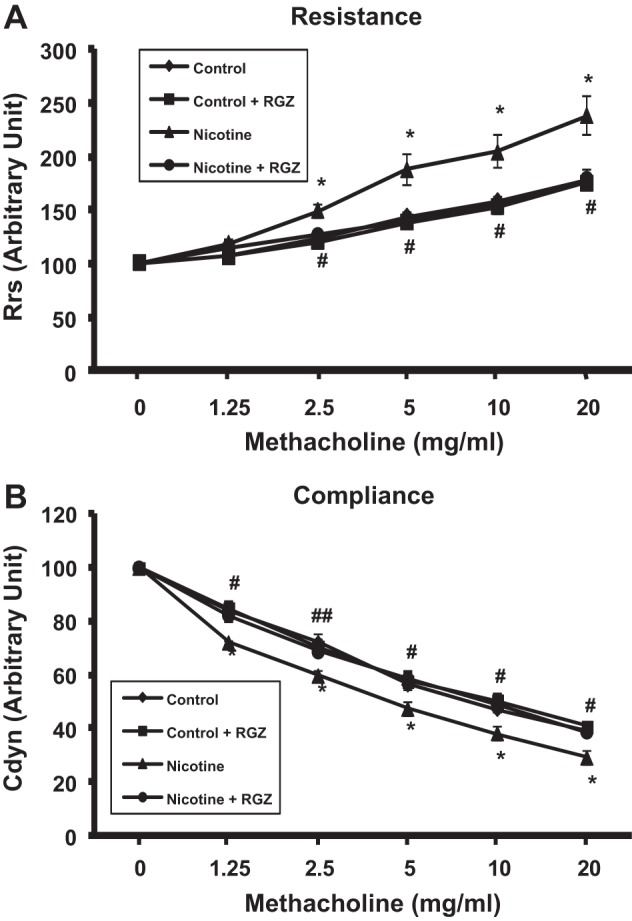
Effect of postnatally administered rosiglitazone (RGZ) on perinatal nicotine exposure-induced alterations in total airway resistance and compliance at baseline and after methacholine (MCh) challenge. Compared with the control group, with nicotine administration there was a significant increase in total airway resistance, both at baseline and following MCh challenge, which was reversed by postnatal RGZ administration. Values are means ± SE. n = 5–6 for each group. *P < 0.05 vs. control; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. nicotine. Rrs, respiratory system resistance; Cdyn, dynamic compliance.
