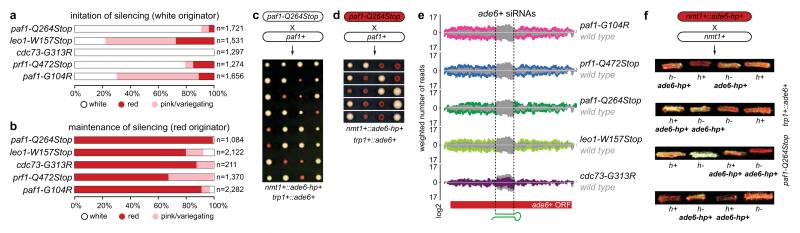
Figure 2. siRNA-mediated epigenetic gene silencing.
a, Percentage of naïve Paf1C mutant cells that establish heterochromatin within 20-30 mitotic divisions. n, number of scored colonies. b, Stability of ectopic heterochromatin in mitotic cells. n, number of scored colonies. c, Initiation of heterochromatin formation during meiosis. Naïve paf1-Q264Stop cells (white) were crossed with paf1+ cells. Spore dissection of 8 crosses is shown. d, Red paf1-Q264Stop cells (heterochromatic ade6+) were crossed with paf1+ cells to assess stability of ectopic heterochromatin through meiosis. White descendants are paf1+. e, siRNA reads mapping to the ade6+ locus in wild type (grey) and Paf1C mutant strains (colored). Read counts were normalized to library size and are shown in log2 scale. Dashed lines mark the ade6+ fragment targeted by the hairpin. f, Red paf1-Q264Stop cells (heterochromatic ade6+) carrying the ade6+-targeting hairpin (ade6-hp+) were crossed with paf1-Q264Stop cells without the hairpin to test hairpin requirement after initiation of silencing. Four spores derived from the cross were struck on YE plate to assess the silencing phenotype. h+ and h- denote mating types and ade6-hp+ marks cells carrying the hairpin.