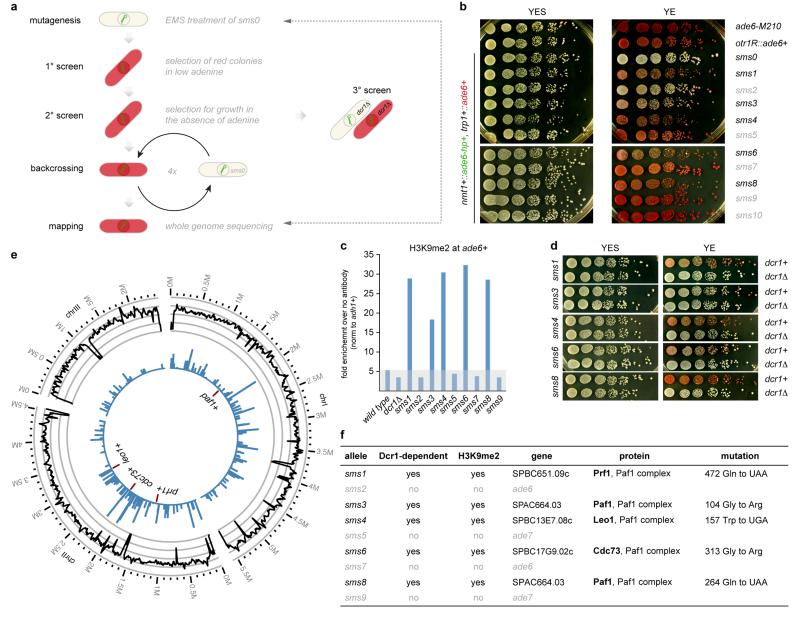
Extended Data Figure 3. Small RNA-mediated silencing (sms) forward genetic screen identifies five true positive hits that enable siRNAs to methylate H3K9 at the ade6+ gene in trans.
a, Workflow of the EMS mutagenesis screen. We mutagenized sms0 cells, which express abundant siRNAs complementary to the ade6+ gene (indicated by green hairpin), with ethylmethansulfonate (EMS) (primary screen). Subsequently, we tested the positive red colonies for growth in the absence of adenine to select against loss-of-function mutations in the adenine biosynthesis pathway (secondary screen). In hits that remained positive after the secondary screen, dcr1+ was deleted to identify truly siRNA-dependent hits (tertiary screen). For mapping of causative mutations by whole-genome next-generation sequencing, positive hits were backcrossed four times. b, sms1-10 mutants show the red ade6+ silencing phenotype on YE plates, which segregated through four successive backcrosses for all 10 mutants. The ade6-M210 loss-of-function allele and ade6+ inserted within centromeric heterochromatin (otr1R::ade6+) serve as positive controls. c, ChIP experiment demonstrating methylation of H3K9 at the ade6+ target loci in sms1, 3, 4, 6, and 8. One representative biological replicate is shown. d, ade6+ silencing in sms1, 3, 4, 6, and 8 is Dcr1-dependent. e, Resequencing of EMS-mutagenized S. pombe strains. From outside to inside, the tracks show the genomic location, the average coverage per window of 10kb (black line, scale from zero to 30), the number of sequence variations identified prior to filtering in all strains per window of 10kb (blue bars, scale from zero to 90) and the five mutations that passed the filtering and overlapped with Paf1C genes (red lines, the two mutations in Paf1 are too close to be resolved individually). f, Table lists mutations mapped by whole genome sequencing. In Dcr1-dependent mutants, we mapped mutations in the genes SPBC651.09c, SPAC664.03, SPBC13E7.08c, and SPBC17G9.02c whose homologues in budding yeast encode for protein subunits of the Paf1 complex.