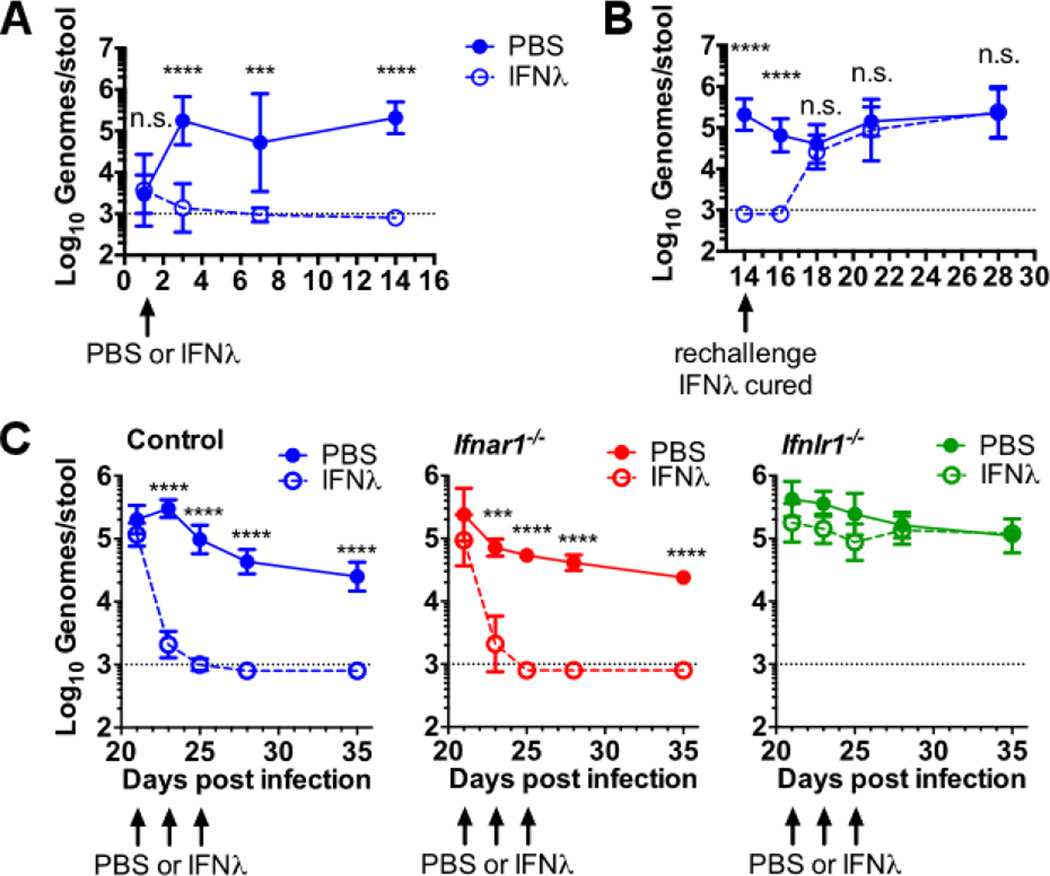
Figure 3. IFN-λ treatment prevents and cures persistent enteric MNoV infection.
(A to C) Feces were collected at the indicated day after oral inoculation and MNoV genomes were quantified by qRT-PCR. (A) Mice were injected with 25 µg of IFN-λ or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) intraperitoneally 1 day after oral inoculation with 106 PFUs of CR6. (B) The IFN-λ-treated mice from (A) were rechallenged with 106 PFUs of CR6 at day 14 after initial infection. (C) Persistent infection with CR6 was established in control, Ifnar1−/−, or Ifnlr1−/−mice followed by intraperitoneal injection of 25 µg of IFN-λ on days 21, 23, and 25. Data shown are pooled from two (A) or three (B and C) independent experiments for a total of four to eight mice per time point. Dashed lines represent limit of detection. Statistical significance was determined by two-way ANOVA. n.s., not significant (P > 0.05); *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, *** P ≤ 0.001, ****P ≤ 0.0001. Error bars in (A) and (B) denote SD and in (C) denote SEM.