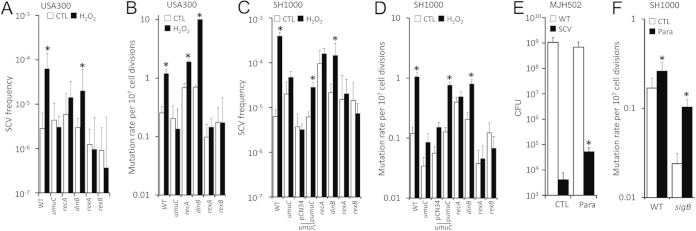
FIG 3.
Expansion of the SCV subpopulation in response to H2O2 requires error-prone polymerase V under the control of the SOS regulon. (A) Frequency of SCVs in populations of WT S. aureus USA300 or transposon mutants lacking functional polymerase V (umuC::Tn), RecA (recA::Tn), polymerase IV (dinB::Tn), or RexAB (rexA::Tn and rexB::Tn) in the absence (open bars) or presence of H2O2 (filled bars). (B) Mutation rate of strains detailed in panel A grown in the absence (open bars) or presence (closed bars) of H2O2. (C and D) As for panels A and B but with strains constructed in the SH1000 background. In addition, panels C and D show data from the umuC::Tn mutant transformed with pCN34 only or pCN34 containing the umuC gene and promoter region (pumuC). (E) Total (WT) and SCV CFU counts from a SH1000-derived sigB mutant (MJH502) grown in the absence (CTL) or presence of paraquat (para). (F) Mutation rate of wild-type SH1000 (WT) and an SH1000-derived sigB mutant (sigB) grown in the absence (open bars) or presence (closed bars) of H2O2. The data in panels A, C, and E represent the mean averages of 12 independent cultures, and error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean. Values in panels B, D, and F represent the mutation rate as determined by fluctuation analysis, and error bars represent the 95% confidence intervals. Values which are significantly different (P < 0.05 [Student t test corrected for multiple comparisons via the Bonferroni method]) in the presence of H2O2 by comparison to those obtained in the absence of oxidants are indicated (*).