Figure 3.
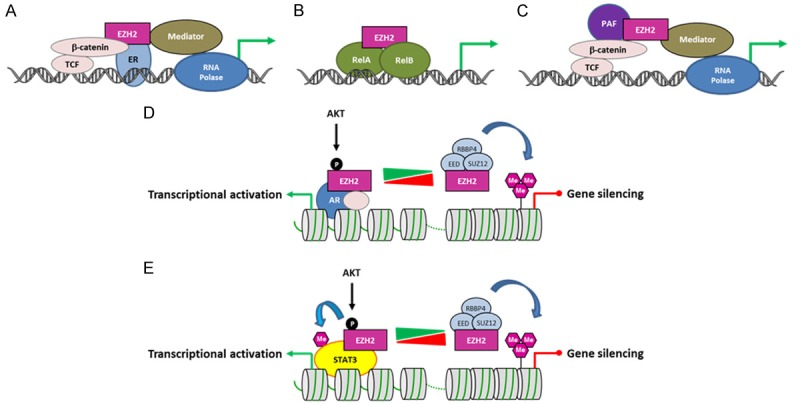
PRC2-independent transcriptional activation by EZH2 in cancer. A. In ER-positive breast cancer cells, EZH2 interacts with β-catenin and ER, and functionally enhances gene expression. B. In ER-negative breast cancer cells, EZH2 interacts with RELA/RELB to stimulate NF-κB target gene expression. C. In colorectal cancer cells, EZH2 forms a complex with β-catenin and PAF to promote transcription. D. In castration-resistant prostate cancer, AKT1-mediated phosphorylation of EZH2 at serine 21 allows EZH2 to interact with the AR at target genes to activate transcription. The AKT pathway then acts as a molecular switch changing EZH2 function from a chromatin silencer to a transcriptional co-activator of the AR. This transcriptional activation function is methyltransferase activity-dependent. E. AKT1-mediated phosphorylation of EZH2 at serine 21 also facilitates STAT3 methylation and activation in glioblastoma stem cells. ER: estrogen receptor; TCF: T-cell factor; AR: androgen receptor; PAF: PCNA-associated factor; RNA Polase: RNA polymerase II.
