Figure 1.
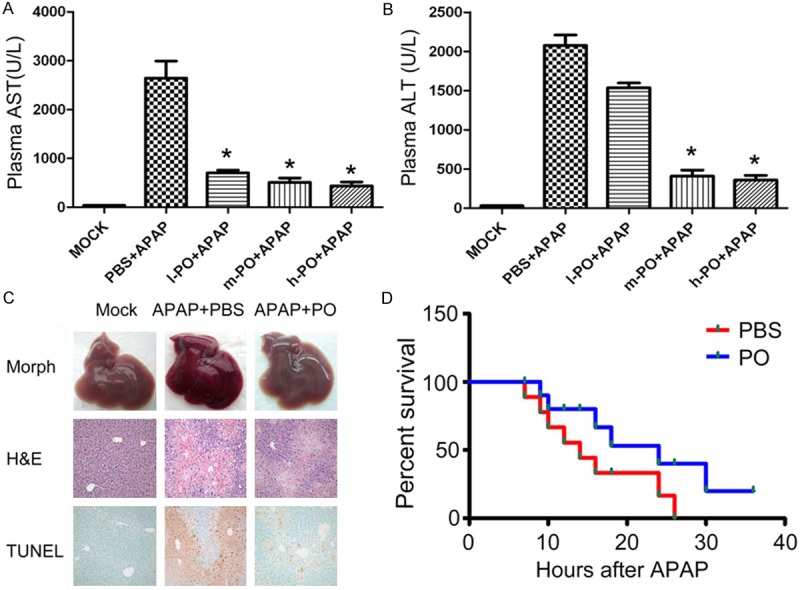
Protective effects of PO against APAP induced mice liver injury. Mice received orally equal volume of PBS and PO one week before APAP intraperitoneal injection. Plasma was taken at 6h after APAP injection. The levels of AST (A) and ALT (B) were detected. l-PO+APAP, m-PO+APAP and h-PO+APAP referred to group administrated PO for 100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg and 400 mg/kg in 0.5 ml PBS, respectively Data were expressed as the mean ± SD (n=5, **P < 0.01 versus PBS+APAP group). (C) Hematoxylin-Eosin (H&E) staining, and DNA fragmentation (TUNEL assay) were observed in three groups (mock, PBS+APAP or PO+APAP animals, original magnification ×100 for H&E and TUNEL panels). (D) Mice were orally administrated with PBS or PO solution followed by an overnight starvation, and then intraperitoneally received APAP dissolved in warm saline (600 mg/kg). Survival of these animals was monitored over 2 days.
